How our Leicester SEO helped iSmart become the most profitable company in Northamptonshire
In 2015 we helped a Northampton-based finance company become the most profitable business in the region. And we worked our way onto on Grant Thornton’s top 200 list using our incredible Leicester SEO powers.
Working with iSmart on SEO, PPC, affiliate marketing and Direct Marketing, we jointly created some best-in-breed campaigns. Of course, not everything worked out. But by working closely we were able to turn their marketing campaigns from a shotgun to a sniper approach which delivered an unrivalled CPA.
CPA
Cost per action, or CPA – sometimes referred to as cost per acquisition – is a metric that measures how much your business pays in order to attain a conversion.
The commercial director had this to say:
dapa have helped put our business in top 5 for profit growth in East Midlands and 1st for profit growth in Northamptonshire for 2015. These guys are the 1% you are looking for…
 We will get back to you ( normally within 10-30 minutes )
We will get back to you ( normally within 10-30 minutes )
Anyway, tell me more about your Leicester SEO…
SEO, a dark art? A mysterious technical process? An expecto patronum spell? No, just hard work and time.
As business owners or managers, you’ve probably heard SEO services come in many forms of white, grey and black to name a few.
Many have tried it themselves, hired internal specialists and employed external agencies with varying results. So, we decided to throw the process of SEO upside down and deliver the results our clients will shout about from the rooftops.
If you’re looking for a Leicester SEO agency that will work with you to meet the goals of your business, get you ranking, traffic and more customers, give us a nudge and we’ll call you back.
Who are you and why should I trust you?
Leicester isn’t our first home. We’ve developed the biggest team in the region in our head office, based in Northampton.
That has enabled us to establish ourselves quickly in Leicester. Most importantly, we’ve got the ability to rank on Google, which is how you found this page we assume?
Not only does this mean we can get people like you to find us on Google but it means our clients will talk about us too. So, a little ‘about us’ while we’re on the subject.
One fine day there was a flourishing finance company, growing fast, with a young whipper-snapper working in the marketing department focusing on SEO.
That company went from forty staff to six-hundred within a year or two and became the most profitable business in the Midlands with great help from its tremendous rankings.
Fortunately for you, the young guy, now twenty-four or so, wanted to own something for himself and parted ways with the then market leading firm.
Three or four years later and millions of pounds spent on unsuccessful search campaigns, the owner of the finance company needed that SEO specialist to help him build once again.
So, together, they created a business to deliver what they both wanted. Now, that business is known as dapa and this is our Leicester SEO branch.
Not quite a fairy-tale. But the difference between the way we approach SEO, and our counterparts, is that we do it for the love. We are great at it and we started in this industry to help others achieve online success.
Enough about you. How can you help me?
Would you ask your web agency to help with your laundry? No. We only do SEO. And I do mean it, if you’re looking for a fancy logo or a new website then we’re going to say no I’m afraid.
SEO is a specialist practice, it’s not a cheap add-on or something a web designer should be doing.
Not because they wouldn’t be great at it – they may well be! But because it’s not their game, it’s not their focus and it’s not their priority.
75% of Google searchers never scroll past the first results page, so we’ll make sure we get you there. If you’re still reading I’ll assume it’s more leads from organic traffic SEO you actually want, so let’s get on to that.
Free SEO Consultation

Come in for a coffee or schedule a conference call with one of our leading UK specialists.
Get Started Now!What Actually Is This Leicester SEO Stuff?
On September 4th 1998 two students changed the world. Segey Brin and Larry Page created Google, the beast we know and love today has evolved many times over the past 18 years (wow – that long? – I feel old now).
Today, 93% of user behaviour starts with an online search. Though big G has evolved beyond recognition almost, the world of SEO hasn’t.
Believe it or not the principals of search (at least in our eyes) have never changed.
To understand that, all you have to do is understand Google’s only job. To give the searcher the result they want or need. That’s it. That one small job made Google a company with a turnover of $100bn in 2016.
The world’s biggest middle man.
So, all we have to do is ensure our website (or our clients’) tops the search results page. Simple right?
Unfortunately, not. SEO is the process of utilising hundreds of key factors that Google wants to see from a market leading website such as yours.
Some websites have the ability to do that more than others, and that’s where our expertise comes in. Basically, ranking is a popularity contest between you and your competitors. If Google believes your website is more popular than theirs, you’ll rank higher.
After all, why wouldn’t they suggest the website that most other people like? If your friend needed their boiler fixing, you’d recommend a reputable engineer, not some obscure randomer.
How does SEO work?
Before we give away our trade secrets it’s important to understand one huge element of SEO. No-one, and we mean no-one, knows 100% how Google works.
To put that into some perspective, if you hired a salesperson, would you know everything about them? Their schedule management, workload, appointments, work process, results, motivation, family issues, what time they’re going for lunch?!
Not to mention you’re probably busy doing other jobs, rather than spending all day brooding over how Google works. Google employs 60,000 people worldwide and has over half a million servers.
As experienced Leicester SEO specialists it’s our job to form our own conclusions, based on experience, testing and constant improvement. That’s what SEO is about and that is what you’re paying for.
Onsite SEO, ticking the boxes
Within your website’s theoretical four walls is everything we class as onsite SEO. Your website itself makes up about 20% of the factors that affect your rankings.
Some Leicester SEO firms will have varying numbers for this, maybe ranging from 5-50% but remember, a lot of this is based on experience so it will vary.
A few things that affect your onsite SEO (without being too technical):
- The amount of times your product/service is mentioned on the pages.
- The position of those words on the page.
- The amount of text vs code contained on each page.
- The URL (site.co.uk/landing-page).
- The Title tag (Top blue line on Google)
- The meta description (the text below the blue line above).
- The filenames of the images you’ve uploaded.
- The load time of each page.
These are a few basics of onsite SEO tactics. To be honest, there’s over a hundred more factors that need to be considered when sculpting every page on your website. It’s massively important to realise that onsite SEO can only get you so far.
Your website will not rank for even mildly competitive searches without links. Many Leicester SEO agencies shy away from building links, so make sure this is part of your campaign before you get started to avoid disappointment.
Link Building, crafting those SEO webs
SEO is a big popularity contest. Offsite (or link building) SEO creates the ‘votes’ Google wants to see in order to decide how popular your website is. The 80% of SEO that is missing, I can hear you wondering, is link building.
Again, many will tell you this number is much higher or lower. In our experience at least, creating links is key to dramatically change your ranking.
Notice how we said change, not improve? Link building can of course be done badly, very badly indeed.
This is the reason a lot of SEO companies have stopped building links completely. We’ve been involved in everything from pure white, off-white and completely black hat link building in our past.
We believe it’s important to understand and spot the dangers of the dark side of the moon.
A bit like taking your car on a skid-pan session, find your limits. A lot of offsite SEO now is done through content creation, PR, blogging and creating pieces that others will link to, effectively doing the SEO for you.
What we have created, through our extensive link building expertise, is a balance between content creation and ‘seeding’ or ‘spreading the word’ about the content we create, i.e. Link building.
Coupling great content with all the right signals Google wants to see is the absolute priority here. Without both, the content (your website) will not rank.
There’s some great examples of how links can bolster a website in our case studies, but here’s a lovely pic to illustrate that point.
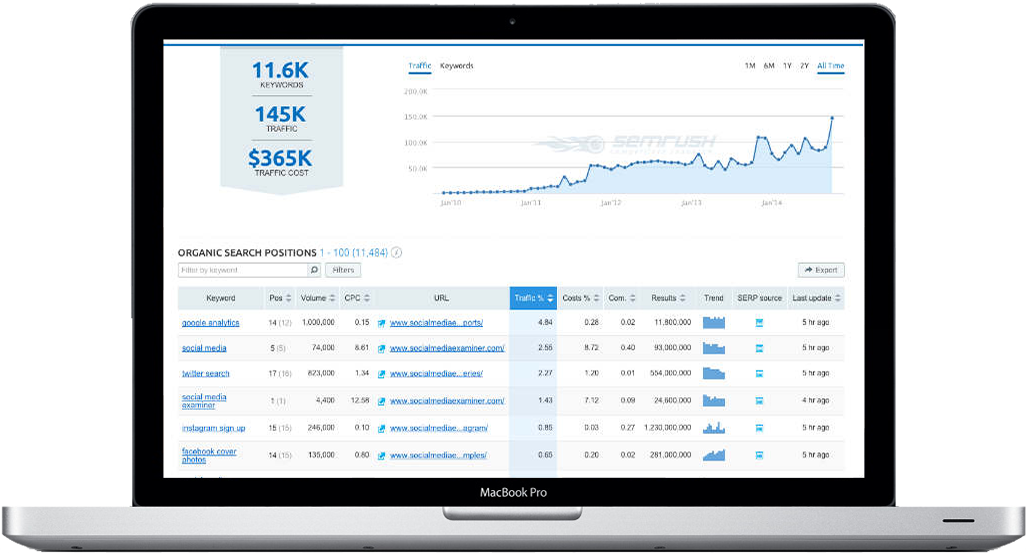
As you can see below, our onsite SEO kicked off in May. Then as we moved in to June and July our link building efforts started to flourish. Effectively onsite SEO gained us around 4% exposure on the market. Not bad at all but could be better.
 Our link building took us to a peak of 27% exposure across all 104 of our keywords and an average rank of under 2 (position 2 on Google).
Our link building took us to a peak of 27% exposure across all 104 of our keywords and an average rank of under 2 (position 2 on Google).
These weren’t your run-of-the-mill long tail keywords either, we’re talking ‘product in location’ where the product was a mainstream financial service. Link building is essential but must be done correctly alongside SEO driven content.
Does my website’s content affect my ranking?
Google has a utility we will call a ‘spider’. A bit like real spiders, it crawls through websites, gathering and analysing information, reading code and words.
Establishing the right balance is key. The ‘spider’ that Google sends around your website and billions of others each day “reads” everything contained on your webpages.
The image below is what it sees:

Through the words you display on your pages the spider will attempt to understand what you’re actually talking about.
Displaying the right information in the right way enables Google to understand and thus rank the website for the keywords you’ve told it to. For example, this page, we want it to appear on search engines for people when searching “Leicester SEO”.
So, zoom out on the page. Press “control + F” on your keyboard, and then type Leicester SEO in the find box. It will highlight all the times we’ve used that term on the page, which is quite a few times as you can see. Couple that with:
- The URL being /Leicester-seo
- The title and description mentioning “Leicester SEO”
- The headings on the page containing the same
This builds up the whole story, it gives Google the knowledge it needs to understand the page’s subject and relevance. Because we know our stuff, hopefully it will rank it well.
To start a Leicester SEO ‘story’ your website needs to display the same criteria as well as other factors to rank each page effectively.
How do I go about finding a Leicester SEO company?
I mean, if you do decide to go down that route, we’re literally right here.
If not, that’s fine, we’re happy as long as you get what you pay for. And we’ll give you some tips to ensure you get the best value for money. Here’s how to decide who you should choose and why.
There’s several ways to go about this. But who you’re looking for is someone who can deliver rankings for your budget and requirements. SEO consultancy isn’t cheap. It takes time, so the first thing to rule out is anything that is cheaper than a couple of hundred pounds per month.
If you can’t afford to invest that amount then SEO really isn’t an option for your marketing, move on, don’t waste your money.
Try your best to avoid those ‘top 10 agencies’ lists. Often these are paid-for privileges and not necessarily a guide of quality.
SEO takes time, so the last thing you want is to get on a mate’s rates tariff and end up being last in line to get the work each month because you’re not spending much.
It happens a lot. Our major tip on choosing a Google SEO agency is to go local and search in your area. Leicester, I assume, will be your choice so here’s what to search in Google (just copy and paste without the inverted commas): “SEO Company in Leicester” or “Leicester SEO Agency”. If you’re looking up a certain agency and they’re not in the first few results, move on.
If you’re looking for a provider then choose one of the top three on the list, start with those that grab you and enquire using their online forms.
Go with those that get back to you quickly as long as the price is right. If they can’t answer their own forms quickly and create an efficient process for doing so, how will they run your campaign effectively?!
What Will SEO Cost Me?
How long is a piece of string? The cost of SEO is dependent on two things – the competitiveness of your market and your ambition.
Generally speaking, a small, local independent service provider will be at the bottom end of the scale. An estimated budget would be around £200 per month.
At the top-end would be a national financial product like loans or insurance which could warrant SEO optimisation budgets of £10k per month plus.
Somewhere in the middle would be your larger local businesses and niche national products/services with an estimated budget of around £1-2k per month.
Your SEO campaign should always be based on your individual goals. You shouldn’t be pigeon-holed into a particular package and be wary of paying too little.
SEO takes time, it takes resource and that costs money. If you’re on a very tight budget and timeline, then using an SEO agency might not be for you.
Free SEO Consultation

Come in for a coffee or schedule a conference call with one of our leading UK specialists.
Get Started Now!What’s the minimum I should spend?
There’s lots of ‘off the shelf’ SEO packages out there designed for mass-market audiences on a budget. This isn’t particularly great. You need a bespoke campaign. That’s definitely a major part of our philosophy at Leicester SEO.
Earlier we discussed how no-one really understands SEO 100%. Now imagine what happens when someone with only a basic competence level starts to build packages for clients.
It can go both ways. You could end up with hugely overpriced campaigns that don’t work. Conversely, automated, hands-off and cheap packages can actually harm your website.
Staying away from those schemes can be difficult. It’s tempting, because as businesses we’re always looking to minimise expenditure and maximise income. Briefly, here’s a quick guide of what to avoid:
- Any form of SEO costing less than £100 per month.
- Yearly packages for a one-off fee.
- Prices based on numbers of links bought.
- Any packages that include paying for links.
Things to avoid in the topsy-turvy world of SEO
We appreciate that SEO isn’t as transparent as many other services, so here’s a quick guide for how to choose the right SEO company in Leicester.
Things you should look for:
- Campaigns that contain an emphasis on link building, content and outreach.
- Companies that rank their own website well in their own region.
- Agencies with clients in Leicester that rank well too.
- Located nearby and will come and see you, or vice versa.
- Someone who answers the phone and helps with your questions.
- Agencies that give you a target rank, traffic or lead KPI.
- Most importantly, someone who has a history of success with relatable businesses.
Now, things you should avoid:
- Any SEO strategy that doesn’t include link building in the proposal.
- Companies that do not rank their own website well in their region.
- Someone who charges less than £100 per month for anything.
- Someone who charges less than £1000 per month for a national keyword.
Here’s one final thought before we crack on with the full guide.
You remember we just told you how to find a reputable SEO company? How did you find this page?
Give us a shout using the form below.
 We will get back to you ( normally within 10-30 minutes )
We will get back to you ( normally within 10-30 minutes )
If you’re looking at learning SEO for yourself, we’ve created this guide for you.
Search Engine Optimisation or SEO is an analytical, technical and creative process which intends to improve the visibility of a website in search engines.
The main objective of SEO is to direct more visitors towards your website which will ultimately translate into more sales for your business. These SEO tips should assist you in creating an SEO friendly website for your business.
Leicester’s best SEO company: how we can help
(I know we like to blow our own trumpet, but we really are quite good – promise!)
Basic, but effective white hat SEO strategies can assist you in driving more organic traffic to your website from a search engine.
Before we go further let’s try to understand what a white hat SEO strategy entails. White hat SEO refers to the use of optimisation techniques, strategies or tactics that are more directed towards the visitors of your website rather than focussing purely on search engines.
Black hat SEO refers to the aggressive use of optimisation techniques, strategies or tactics that focus solely on search engine rankings rather than the visitors of your website and in the process tend to disobey the search engine guidelines.
Black hat SEO might give your website some immediate success through improved traffic but, in the long run can get your website banned from Google and other search engines.
Penalties awarded by Google for failing to adhere to its guidelines can have a severe long term impact on search rankings for important keywords and traffic to your website.
So, it is best to steer clear of SEO techniques that can be described as ‘grey hat’ because you never know, what grey hat is today might be deemed black hat tomorrow, by Google. Next we’ll answer some common questions that people have when starting out in SEO.
What are the ‘rules’ for SEO?
Google emphasises the need for webmasters to adhere to their guidelines. And as a result, it rewards the websites providing high quality content and exceptional white hat SEO strategies to obtain high search engine rankings.
Google also punishes websites that are disobeying Google specified guidelines, even if these sites initially ranked highly.

While these ‘rules’ are not laws as much as guidelines, it is important to remember that these guidelines are laid down by Google. It also should be noted that some methods used to achieve higher rankings in Google are considered illegal.
For example, hacking is considered illegal in the UK as well as in the US. The decision to abide by these guidelines or to bend or ignore them rests with you- all providing varying levels of success or retribution from Google’s spam team.
What you will read here falls within the Google recommended guidelines and will assist in boosting traffic to your website through natural or organic SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages).
Definition of SEO
SEO entails getting free traffic from Google, the most popular search engine in the world.
Finding opportunities for your business
To understand the art of SEO it is important to consider two factors.
Firstly, with what intent will target audience harbour in their business search for queries? And also, what type of result will Google provide to its users when a particular search query is typed?
It is about assembling a lot of factors to create opportunities for your business. Any good optimiser should have a deep understanding about how search engines like Google generate their natural Search Engine Result Pages (SERPs) to satisfy any informational, transactional and navigational queries that a user might have.
Risk management
A good SEO marketer should have a strong grasp on the following:
- The short term and long term risks involved in optimising search engine rankings
- The type of site and content Google wants to return in its natural SERPs.
The objective of any SEO campaign is to create greater visibility for a website in search engine results. Now, this should be a fairly simple process if it were not for the many difficulties that lay in the way.
There are rules or guidelines that needs to be followed, risks to take and battles to be won (or lost) as part of an SEO campaign.
Free traffic
Ranking high on Google search engines is very valuable for your business. Think of it as free advertising for your brand.
Free advertising that is provided on perhaps the most invaluable advertising space in the world. Traffic from Google SERPs is still considered the most valuable source of organic traffic (traffic that your website receives due to an unpaid search result) for a website.
 It can be the deciding factor in determining whether a website or an online business is successful or not. The fact is that it is still possible to generate free, highly targeted leads for your business by simply optimising the content on your website to be as relevant as possible for a potential customer who might be on the lookout for a product or service that your company provides.
It can be the deciding factor in determining whether a website or an online business is successful or not. The fact is that it is still possible to generate free, highly targeted leads for your business by simply optimising the content on your website to be as relevant as possible for a potential customer who might be on the lookout for a product or service that your company provides.
As you might have already guessed, there is a lot of competition today for that free advertising space, sometimes even from Google itself.
However, it is important to note that it is futile to compete with Google. Instead focus on competing with your competitors.
SEO: the process
The process is something that can be practiced anywhere, be it your bedroom or your workplace.
Traditionally it involves multiple skills such as the following:
- Website design
- Accessibility
- Usability
- User experience
- Website development
- PHP, HTML, CSS, etc.
- Server management
- Domain management
- Copywriting
- Spreadsheets
- Backlink analysis
- Keyword research
- Social media promotion
- Software development
- Analytics and data analysis
- Information architecture
- Research
- Log Analysis
- Looking at Google for hours on end
Yes, it takes quite a lot to rank high on Google SERPs in competitive niches.
Is user experience important?
If you expect to rank high on Google SERP’s in 2018, then make sure you provide your visitors with an enjoyable experience. Rather than focussing on manipulation or old school techniques to boost your rankings.
Does a visit to your website provide your users with a quality experience? If not, then it is better to start doing so or Google’s Panda algorithm will be out to get you and your site.
As Google keeps raising the bar for what it considers to be quality content year-on-year, it’s important to provide your users with a great experience when they visit your website. Not just with content but with pages that are easy to find, appealing multimedia and a sleek web design.
The success of your online marketing strategy can be dependent on the investment in the following:
- Higher quality on-page content on your website.
- Website architecture and its usability.
- Conversion to optimisation balance and
- Promoting your website.
What is a successful SEO strategy?
Simply put, relevance and trust are vital to the popularity of your website online. The tolerance of manipulation has passed. In 2018, SEO will be about adding useful, relevant and quality content to your website that meets a definite purpose and also provides a high quality user experience.
SEO is not for short term benefits. If you are serious about getting free traffic from SERP’s then be ready to invest sufficient effort and time into your SEO campaign.
Quality signals
Google will rank your website high if you are prepared to add high quality content to your website thereby creating a buzz about your brand. It might help you win backlinks from reputable sources, too.
If your SEO strategy revolves around manipulations or skirting around the boundaries of Google recommended guidelines, then the likelihood of being penalised by Google will be very high. Any penalty from Google will last until you fix the offending issue, which can sometimes take up to years.
For instance, backlinks are weighed ‘far too’ positively by Google to drive a website to the top position of a SERP.
That is why black hat SEO users do it, as it is the easiest way to rank a website on a search page. If you intend to build a brand for your business online, then it is important to remember that you shouldn’t use black hat methods.
Why?
Because, if using black hat SEO methods has got you a penalty, then merely ‘fixing’ the problems that are in violation will probably not be enough to recover the organic traffic to your website.
Recovering from a penalty is as much a ‘new growth’ process as it is a ‘clean up’ process for your website.
Google rankings constantly flap about
Google updates its index of websites once every month. However, since 2002, Google search results started changing in between updates.
This continuous change of search results came to be known as ‘ever-flux’.
Remember, it is in Google’s best interests to make SERP manipulation as difficult as possible.
So, every once in a while, the people at Google responsible for the search algorithms modify the rules a wee bit. Not only to improve the quality standards of the pages that contend for the top rankings, but also to ensure that the pages stay updated and relevant.
Just like the Coca-Cola Company, Google likes to keep its ‘secret recipe’ under lock and key. Therefore, they might sometimes offer advice that is helpful or in some instances offer advice that is just too vague to configure.
Some advice might just be to misdirect SEO optimisers from manipulating search engine rankings into their favour.
Google has gone on record to say that their intent is to frustrate SEO optimisers who look to increase the volume of quality traffic to their website, through the use of low quality strategies which are classed as web-spam.
However, at its core SEO is still about the following:
- Keywords and quality backlinks
- Reputation, relevance and trust
- Quality of content and visitor satisfaction.
The key to creating a SEO strategy that works is by making sure that you provide your visitors with a great experience.
Authority, relevance and trust
The key aspect of optimising a webpage includes ensuring that all the content on that page is trusted and relevant to rank for a specific search query.
It is all about ranking for keywords on merit over a long period of time and not through manipulation of Google specified guidelines.
To do so, you should follow the white hat rules laid down by Google which strives to build the trust and authority of your website (and brand) naturally over a period of time.
Depending on the route you take for the SEO of your website, remember that if you are spotted by Google for using manipulative SEO techniques, then your website will be classified as spammy and as a result you will be punished for it.
If your website has been penalised, then sometimes it can take years to address the violations and overturn the penalty.
Simply put, Google does not want anybody to manipulate their search rankings easily as it can be quite a dampener on their own objective of having you pay them for using Google Adwords.
Ranking high organically on Google listings can be viewed as real social proof for a brand or business, a way to steer clear of PPC (pay per click) costs and also the best possible way to drive valuable traffic to your website.
The objective of doing SEO is making sure that you rank high organically on SERPs without incurring any additional expenditure.
Is user experience an important factor?
When Google released its quality guidelines, the phrase ‘user experience’ is mentioned in its about 16 times.
However, Google maintains that user experience is not as yet considered a’ classifiable ranking factor’ for desktop searches at the very least.
For mobile searches, it is a whole different ball game as UX (user experience) is usually the basis of any mobile friendly update.
Even if UX is not considered a ranking factor, it can be handy to understand what exactly constitutes as ‘poor user experience’ in Google’s eyes because, if your website contains poor UX signals which have been identified by Google, then you can be sure of the fact that it will affect the rankings of your important keywords.
What constitutes a bad user experience?
For Google, rating user experience for a website from the perspective of the quality guidelines revolves around marking the page down for the following:
- Website design that is misleading or potentially deceptive
- Sly redirects
- Spammy user generated content and harmful downloads
- Low quality main content or MC on the landing page of your website
- Low quality supplementary content or SC on any page of your website
What is supplementary content (SC)?
For a web page to have a positive UX, Google mentions the importance of using useful and functional supplementary content.
Supplementary content contributes to an improved UX on a webpage even though it cannot directly help a page reach its ranking objectives.
Webmasters create and use SC as an integral part of improving the user experience of a webpage.
A common example of SC is inserting navigational links that help your visitors access other parts of your website. In some instances, the content behind the tabs are also considered as part of the supplementary content of that page.
Not having SC on your webpage or using SC that is not helpful to your visitors can contribute towards a ‘low quality rating’ for your webpage.
This low quality rating is also dependent on the type of website and the purpose of the page.
Small websites that usually exist to serve their communities are judged by different standards when compared to larger websites that have a number of webpages and content.
For PDFs or JPEG files no SC is needed or expected. It is important to remember that no amount of SC can help you if the main content (MC) on your webpage is of poor quality. Important points about SC:
- Supplementary content can be largely responsible in making a high quality page more satisfying for a visitor.
- Your SC should be relevant and most importantly it should ‘supplement’ the MC on the webpage.
- Smaller websites might not require using as much SC on their webpage as compared to large websites.
- A page can still be ranked very highly on a Google SERP without using any SC.
Google expects websites representing large companies or corporations to devote a lot of time and effort into creating a great user experience for visitors with the help of relevant SC.
On such large websites, SC may be the main way through which visitors can explore the site further and gain access to MC. Such websites also tend to be content intensive. Therefore, the lack of helpful supplementary content can lead to a poor rating.
If it becomes difficult for a visitor to access the MC of a website because of deliberately designed ads that intend to distract the visitor, it affects the overall quality of user experience of that page which could be a reason for a low rating.
Despite the importance of SC, Google is considerably more interested in the MC of your webpage and the reputation of the domain on which the page is on, with regards to your site and also competing pages from alternative domains.
Targeting conversions with user experience and usability
Consider pop-up windows as an example: Jakob Nielsen, a renowned usability expert, stated that 95% of web visitors were annoyed by unnecessary and unexpected pop-up ads, especially the ones that contained unwelcome advertisements.
Pop-ups have been consistently voted as the most hated advertising technique used online. Web accessibility students would probably also agree on the following:
- A new browser window should only be created if the user wants one.
- Pop-up windows should not mess up the screen of a visitor or a prospective client.
- By default, all links should remain open in the same window. However, a possible exception to this can be if one of the pages opened contains a list of links. In such a scenario, it is advisable to open the links in a new window as it allows the user a chance to return to the original page containing the link lists easily.
- Make your visitors aware that by clicking on something they could be about to invoke a pop-up window.
- Employing too many pop-up windows on a webpage can have a disorienting effect on the user.
- Preferably provide your user with an alternative to clicking on a link that could possibly open a pop-up window.
A pop-up window can be a hindrance to web accessibility, but the fact is it can provide an immediate impact and as a result it can be foolish to dismiss a technique that has a proven track record of success.
Also, there are very few clients that would choose accessibility over increased sign-ups that using a pop-up will provide for a website.
Generally, it is recommended that you do not use a pop-up window on days when you post a blog in your website as it severely affects the likelihood of your blog post being shared on social media circles by your readers.
Interstitials on a mobile site can be extremely annoying for a visitor and it also affects the user experience of that page. What is an interstitial?
It is the ad that appears when the original page you clicked on is still downloading.
Google announced that any mobile page that displays an interstitial which hides a high proportion of MC (main content) after November 2015 will not be considered as mobile friendly, as it significantly affects the user experience of visitors on that mobile web page.
Although, webmasters are still allowed to use interstitial banners of their own implementations as long as they do not block a large chunk of the page’s content.
If Google thinks that the use of an interstitial is severely affecting the user experience of your visitors, then it can be bad news for your rankings.
Mobile web browsers on the other hand can provide alternative ways to promote an app without affecting the user experience of a visitor on the page.
If you are still adamant about using a pop-up window, then instead look to insert one as part of the exit strategy of your page.
So, hopefully by the time a visitor comes across a pop-up window they are not annoyed by it, but instead intrigued by the quality of the main content on your page.
This can be a great way to increase the number of subscribers to your site with a similar, if not better conversion rate than pop-ups.
For any SEO optimiser, the priority should always be to look to covert customers without having to revert to techniques that affect their Google rankings negatively.
In your rush to boost your rankings or converting leads into sales, do not forget the primary reason why a visitor has landed on your page in the first place.
If you do so, then you might as well place a big target sign over your website for Google to ‘get’ you.
Free SEO Consultation

Come in for a coffee or schedule a conference call with one of our leading UK specialists.
Get Started Now!Remember, Google wants to rank only high quality websites
Historically, Google looks to classify sites in its ‘directory’ of sorts, sorting sites into categories. Now, whatever that may be for your site, you do not want your site to get tagged with a low quality label irrespective of whether it is put there by a human or a Google algorithm.
While human ratings might not directly affect your site’s rankings, it is still best to avoid anything that can be used by Google to assign your site a low quality label.
‘Sufficient Reason’
Now, you will come across these two words quite often in the quality guidelines. In some scenarios there could be ‘sufficient reason’ to mark a page down immediately on certain specific areas.
Here we take a look at excerpts from the quality guidelines that specifically relate to these two words:
- An unsatisfying amount of MC (main content) on a page is ‘sufficient reason’ to give that page a low quality rating.
- Low quality MC on a page is ‘sufficient reason’ to give that page a low quality rating.
- Any page that lacks the appropriate E-A-T (Expertise Authority Trust) provides ‘sufficient reason’ to give it a low quality rating.
- Negative reputation is ‘sufficient reason’ to give a page a low quality rating.
According to Google, MC should be the primary reason why a page exists.
Here are some reasons why the MC of your page can be the main cause of your poor quality rating:
- The quality of MC on the page is low.
- An unsatisfying amount of MC is used for the ‘purpose’ of the page.
- There is inadequate information provided about the website.
This will affect the user experience of your visitors and thereby affect your rankings.
Poor quality MC is perhaps the biggest factor for your page being assigned the lowest possible quality rating by Google.
Additionally, if you use pop-up ads that block a major portion of the MC on your page then it contributes towards poor user experience and as a result your rankings will suffer.
Generally, pages that provide visitors with poor user experience will receive low quality ratings.
For example, if a page tries to download malicious content or software’s then, it will be given a low quality rating even though it might contain images that are related to the search query.
If the page is designed poorly or in a way so as to deflect attention away from the MC, it will be given a poor quality rating.
If the design of the page is lacking say in terms of page layout or the use of space in a page that is intended to distract from the MC on the page, it is assigned a poor quality rating.
The following are given most significance in determining whether or not the page is a high quality one after on page content:
Poor secondary content
Here are some reasons why the secondary content on your page might be considered of a low quality level:
- The SC used on the page is distracting or unhelpful because it is intended to benefit the website rather than the user.
- The SC used is distracting or unhelpful for the purpose of the page.
Poor secondary content can lead your page being marked with a low quality rating.
Distracting ads
For example, an ad depicting a model in a bikini might be appropriate if your site is about selling bathing suits.
But if that is not the case, such an ad can be highly distracting for a visitor who has landed on the page for some other reason. Therefore, it affects the quality of user experience your page is providing.
As a result, your site might be handed a poor quality rating by Google.
Poor maintenance
Not maintaining the website properly or updating it on a regular basis could be another reason for a poor quality rating.
SERP sentiment and poor user ratings
If your website has a negative reputation, it could be given a low quality rating even though it might not have malicious software in it or indulge in financial fraud.
This is especially true when it is an YMYL (Your Money Your Life) page.
Lowest rating
You would probably have to do a lot of things wrong simultaneously to be handed the lowest rating.
Throughout the quality document you will come across the phrase “should always receive the lowest rating” quite often.
That is one direction you should look to avoid at all costs for your website.
So, when does Google assign a page the lowest quality rating possible?
The statements mentioned below should give you a fair idea:
Websites or web pages that lack any sense of purpose.
YMYL websites that consists of pages with insufficient or no information about the website.
Websites or web pages that are created to make money while making no effort to help users.
Pages with low quality MC such as a webpage created without any MC. Pages with no MC usually lack any purpose or used for deceptive purposes.
Pages that are intentionally created with bare minimum amount of MC or with MC that is irrelevant and thus unhelpful for a user.
The MC is copied entirely from another source with little or no efforts paid to providing value for users. In such a scenario the page will be assigned the lowest quality rating possible even if the source of content is credited to the original source.
The pages originate from hacked, defaced or abandoned websites.
Pages that consist of content that lacks authority or is considered unreliable, untrustworthy, misleading or inaccurate.
A Page or website that is harmful or malicious in nature.
Websites with a malicious or negative reputation. Proof of fraudulent or malicious behaviour is reason enough for it being granted the lowest rating possible.
Deceptive webpages or websites that ‘appear’ to provide helpful information but, are in fact created for other purposes with the intention to deceive or harm users for personal gain, will be handed the lowest rating possible.
Pages that are designed with the intention of manipulating users into clicking certain links with the assistance of visual design elements such as page layout, link placement, images, font colour etc. will be considered as deceptive page design and thus be penalised with the lowest quality rating.
The pages just do not ‘feel’ trustworthy and appear to be fraudulent in the eyes of Google will be given the lowest quality rating.
Pages that ask for personal information without providing a legitimate reason for the same or websites that ‘phish’ for passwords will be handed the lowest quality rating.
Websites lacking proper maintenance are rated poorly
Your website would be given a low quality rating if your site consists of broken links, images that do not load or content that is outdated or stale.
Non-functioning or broken pages are rated poorly
Google provides clear guidelines on how you can make your 404 pages more useful:
- Make sure that you convey to your visitors that the page they were looking for could not be found in a clear manner.
- Create 404 pages using language that is considered inviting and friendly.
- Make sure that the 404 page you have created retains the same look and feel as the rest of your site.
- Contemplate linking your most popular blogs or articles and also provide a link to your site’s home page.
- Ensure that you provide your user with a way to report any broken links in your website.
- If a missing 404 page is requested, then make sure your web server returns a 404 HTTP status code.
How are pages with error messages or no MC rated?
Google does not index pages that do not have a specific purpose, relevant or inadequate MC.
A well created 404 page along with the proper setup goes a long way in preventing this from happening. Some pages when clicked on load with content that is created by the webmaster but, at the same time display an error message or have missing or insufficient content.
There can be many reasons why a page loads with insufficient content.
For example, if a site has a broken or dead link then, that page does not exist anymore and as a result the page will load with an error message displayed on it.
Now, it is normal for websites to have a few pages that are non-functioning or broken.
But, if you do not take steps to remedy it immediately, those pages will be given a poor quality rating even if all the other pages on the website are of the highest quality possible.
According to Google’s John Mueller, 404 errors on invalid URLs do not affect the ranking or indexing of your site in any way.
We always advise our clients to not ignore broken links on their site and to take remedial steps to deal with such pages properly.
By doing this ‘backlink reclamation’ you reclaim ‘equity’ that you thought you had lost but it still gives your site great value with regards to its rankings.
A lot of broken links flagged by Google are found to be irrelevant and inconsequent with regards to your search engine rankings.
So, it is important to first single out the links that are affecting your rankings and remedy them.
Luckily, finding broken links on your site is relatively easy as there are many SEO tools available to help you with it.
We still believe in the effectiveness of analytics and prefer to use it to look for dead or broken links especially if the site has a history of migrations.
In some scenarios, crawl errors are detected if there are structural issues within your CMS or website.
How can you be sure about it? Easy, by checking the origin of the crawl error, double check if necessary.
If you detect a broken link on your site within your webpage’s static HTML, then it is always advisable to fix it.
If Google algorithms like the content uploaded on your site, it might explore further to discover more great content from your website.
For example, by looking to find new URL’s in JavaScript.
So, if a new URL is tried out but, the URL displays a 404 message then, you miss out on a valuable opportunity to boost your rankings.
The quality guidelines can be a great reference point for you in terms of how you can avoid getting low ratings and potentially avoid any punishments from Google.
Google won’t rank your site if you have low quality pages when it has better options
With exact matches to key search terms, even then those pages might not rank highly in 2018 if it does not have all the remaining important ‘ingredients’.
Usually, Google would prefer sending long tail search traffic like a user searching for something using voice search on their mobile, to pages that offer a high level of quality and clearly explains a topic or concept, its connections with relevant sub-topics rather than, send that traffic to a website with low quality pages just because they have used the exact search phrase on their page.
Identifying dead pages
If a large portion of content you have submitted as part of an xml sitemap is being de-indexed by Google, then there might be a problem with your web pages.
How will you find out the pages that are not being indexed by Google? We look to identify the problem using a performance analysis.
This involves assembling data retrieved from a physical crawl of your website with the assistance of webmaster tool’s data and analytics data.
It is possible to identify the type of pages the CMS generates by conducting a content type analysis.
Such an analysis will also help in evaluating how each section of your website is performing.
Let us assume that you have about 1,000 pages of content on your website.
Now, if only 10 out of these 1,000 pages is generating organic traffic for your website in a span of 3 to 6 months, then you can consider the remaining 990 pages of your site as worthless with regards to your SEO goals.
If these pages were of high quality, then they should have been generating traffic for your website. But as they are not doing so, we can safely assume that the quality of these pages is not of the standards that Google desires.
Thus, by identifying pages in your website that do not generate any traffic over a specific timeframe from those that obviously do, you can easily clean up a large chunk of redundant URLs from your website.
Technical SEO tutorial
Here at dapa, we like to put our ‘Google Search Engineer’ hat on when we conduct SEO audits for our clients, as we have found it to be one of the best ways to provide value to our client which could benefit them over a long period of time.
Google has a rather long list of technical requirements that it “advises” any website owner to meet.
Additionally, they also provide a pretty exhaustive list of things you cannot do if you want to rank high on a SERP.
Adhering to all of Google specified guidelines is no guarantee of success, but not following them can be a sure-fire recipe for poor rankings in the long run.
If there is an odd technical issue then it can actually seriously affect your entire site, especially if the issue is rolled out across many pages.
The advantage of following all of Google’s technical guidelines is often secondary.
It might not boost your rankings, but it will prevent your website from suffering major setbacks such as penalties or not getting filtered by Google’s algorithm.
So, if your competition falls, your website rises in the rankings naturally, as a result.
Mostly, your website’s rankings will not suffer due to individual technical issues but, by addressing those issues you can enjoy many secondary benefits.
Also, if your website has not been marked down by Google then it is not demoted and as a consequence it climbs up the rankings.
We believe that the most sensible thing to do in such a situation is to not give Google a reason to penalise or demote your site.
Employing such a strategy might involve investing for the long term but over the years we have found it to be one of the most effective ways to rank on page 1 of a Google SERP.
What is Domain Authority (DA)?
Domain authority (DA) as Moz.com refers to it, is a very important ranking factor.
But, what is DA exactly?
One thing we can be certain of is that there is no ‘trust’ or ‘authority’ rank which Google uses to evaluate the pages on your website.
Page rank can be considered as an important factor that helps build trust about your website in the eyes of Google. It depends on the number of links your website has and the quality of those links.
If your website receives a lot of high quality external links, then it earns trust with Google and is therefore ranked higher.
DA is more about comparing with sites that are already popular, trusted and reputable. Reputable sites usually have a high DA score, with several backlinks of similarly impressive DA.
That is why link building has always been a popular SEO tactic.
Counting the number of links your website has and the quality of those links is usually how third party tools evaluate a website’s DA.
In the past, massive trust and DA ranks were awarded to websites that had gained a lot of links from reputable sources and other online businesses with high domain authority ratings.
At dapa, we associate DA and trust based on the quality, type and number of incoming links a website has.
Examples of trusted domains include the W3C, Wikipedia and Apple.
How can you position your site as an Online Business Authority or OBA?
The answer to that is quite straightforward actually:
By offering a killer online product or service and backing it up with a lot of useful and high quality content.
Sounds simple enough doesn’t it? But executing it can prove to be anything but straightforward.
If you have successfully managed to establish your site as an OBA, then how can you capitalise on it?
There are two ways you can go about it.
You can either turn your site into an SEO black hole (usually applicable for only the biggest brands) or you keep churning out high quality informative content all the time.
Why?
Because Google will always will rank it!
Is it possible to imitate an OBA on a much smaller scale and in specific niches by identifying what it does for Google and why Google ranks it highly?
Yes, but it takes a lot of time and work.
Recreating the same level of service, experience or content even on a much smaller scale can be anything but easy.
Over the years, we have found that focussing on content is the easiest and perhaps the most sustainable way through which a business establishes itself as an OBA in a particular niche.
Along with that systematic link building and promotion of what you are doing can go a long way in helping your website achieve its objectives.
Brands are the solution, not the problem
Creating a brand for your business online will help in distinguishing you from your competition.
If you are a brand in your particular niche, then Google would prefer to rank you over your competition as it would ‘trust’ you to not spam or use dummy content and in the process reflect poorly on Google.
Moz gives a high DA score to websites they trust, which gives them a considerable boost in converting leads into sales.
Now, unless you are creating high quality original content, make sure that you create content that is specific to your topic.
Also, if your website gets links from sites that are thought of as brands in their respective niche then it counts as a quality backlink and will boost your rankings.
It is easier said than done but that should be the focus of your SEO strategy.
You should always look to establish your main site as an online brand.
Does Google have a preference towards bigger brands in organic SERP’s?
Er, yes.
There is no denying that bigger brands have an advantage over smaller upcoming businesses in Google’s ecosystem.
Also, Google can try to “even” out this disparity by encouraging smaller brands to pay more on Google Adwords.
However, a small business can still achieve success online as long as they focus on a long term strategy prioritising depth and quality with regards to how the content is structured on the website.
How important is domain age as a Google ranking factor?
No, not really. For example, if your website is hosted on a ten year old domain that Google has no idea about then it is similar to having a brand new domain.
On the other hand, if your website is hosted on a domain that has been continuously cited year on year and as a result developed a reputation of trust and authority then it is very valuable in terms of your SEO techniques.
But again, it is important to remember that the ranking benefits you might enjoy as a result of hosting your website on a reputed and trusted domain are not solely because of the ‘age’ of your website. Therefore, the focus should always be on creating great content and having high quality links to your site.
A year old domain cited by reputed and authoritative sites is probably more valuable in terms of your search engine rankings when compared to a ten year old domain with no search performance history and no links.
We also believe that without first considering ‘ranking conditions’, you cannot discover ‘ranking factors’ for your website. Other important ranking factors include:
- Domain age, not on its own though.
- The amount of time you have registered your site domain for. Again on its own this should not be thought of as a vital ranking factor. It is common knowledge that valuable domains are sometimes paid for many years in advance whereas backdoor or illegitimate domains are seldom used for more than a year. Paying many years in advance for a domain is usually just a method employed to prevent others from using that domain name and does not in any way signify that you are doing something that is very valuable in the eyes of Google.
- The domain registration information, especially if it was kept hidden or anonymous.
- TLD or top-level-domain of your website. TLD is the last segment of your domain name which follows the final dot in your website’s internet address. For example, .com versus .co.uk or .com versus .info. TLD helps to identify what your website is associated with such as, the purpose of the site or organisation that runs it or the geographical area from where it originates.
- Root domain or sub domain of your website.
- Domain past owners. For example, how often the owners have changed for a particular domain.
- Domain past records. For example, how often the IP has changed for a particular domain.
- Keywords used in the domain.
- Domain IP
- Domain IP neighbours.
- Geo-targeting settings in Google Webmaster Tools.
Google penalties for Black Hat SEO techniques
In 2018, you need to be more careful about the methods you employ to boost your SEO rankings.
You might run the risk of falling under Google’s radar if they smell any foul play, which can increase the chances of penalties.
The Google web spam team are currently on the warpath in terms of identifying sites that use unnatural links along with other tactics that intend to manipulate the SERP rankings.
Google is trying to ensure that it takes longer to achieve results from black and white hat SEO optimisation techniques and also remains intent in creating a flux in its SERPs, based on the location of the searcher at the time the search query is typed and whether or not a business is located near the searcher.
To improve your rankings, there are still some factors that you cannot influence legitimately without risking a penalty.
While saying that, it is still possible to drive greater traffic to your website using many alternative techniques.
Ranking Factors
Google literally considers a hundred different ranking factors with signals that can change on a daily, monthly or yearly basis to help it sort out where your page should rank in comparison to other competing pages on a SERP.
Many ranking factors are either on site or on page while others are off site or off page.
Some ranking factors are based on where the searcher is located at the time of typing the search query or depends on the search history of the searcher.
At DAPA, we use our experience and expertise to focus on strategies that provide the best Return on Investment for your efforts.
Learn SEO basics
If you are starting out it is important to not be too brash with your SEO strategy believing that you can deceive Google or its algorithms all the time.
It is best to keep your strategy basic and focus on the E-A-T (Expertise Authoritativeness Trustworthiness) mantra that Google keeps advocating.
Direct your energy into ensuring a great user experience.
Always, always use SEO techniques that fall within Google Webmaster Guidelines.
Be clear right at the outset about the SEO company tactics you are going to employ and then stick to it patiently.
This will ensure that you avoid getting stuck in the midst of an important project.
If your objective is to deceive the visitors who land on your site through Google, then remember that Google is not your friend.
Google will send a lot of free traffic your way, if you manage to reach the top of a SERP. So, following Google recommended guidelines can be very beneficial.
There are a whole lot of SEO techniques that are effective in terms of boosting your site’s rankings in Google but are against their specified guidelines.
For example, many links that at one time helped your site reach the top of a SERP might today be hurting your site and its chances of ranking high on a SERP.
Keyword stuffing is one such black hat SEO technique that might be holding your page back from achieving the desired ranking on a SERP.
Link building should be done in a smart and careful manner, such that it does not put you on Google’s radar, thereby reducing the likelihood of your site being penalised.
Do not expect instant results or to rank high on a Google SERP without first putting in the necessary amount of investment and work.
You do not have to pay anything to get your site into Google, Bing or Yahoo. Major search engines will discover your website pretty quickly by themselves within a few days.
This process can be made easier if your Content Management System or CMS, ‘pings’ search engines whenever content is updated on your site. For example, using RSS sitemaps or XML to do so.
The eternal importance of backlinks
Apart from how relevant your website is, Google will rank it based on the number of incoming links to your site (amongst hundreds of other metrics) from external sites and the quality of those incoming links.
Usually a link from another site to your own site acts as a vote of confidence for your webpage in the eyes of Google.
Now as the page continues to receive a high number of links, it earns more trust in the eyes of Google, which translates into higher rankings for your page.
If a highly reputable site links to your webpage, then you get a quality backlink.
The amount of trust Google has on the domain of your website will also affect how it will be ranked. Backlinks from other websites is perhaps the most crucial part of how your site will be ranked on a SERP and it trumps every other ranking factor that is considered by Google.
High quality content produces high quality results
One of the easiest ways to rank quickly is by creating original high quality content. Search engines always tend to reward websites that provide original content – the kind which has not been seen before.
For starters, these pages are indexed very quickly. Ensure each of your pages has sufficient text created specifically for that page.
This way you can get your pages ranked quickly without having to jump through hoops to do so. If the content on your website is original and of a high quality, it is possible to generate quality inbound links or IBL to your site.
Now, if the content used on your website is already available on other platforms, you will find it difficult to get quality inbound links, as Google prefers variety in its results.
Also, if you use original content of a reasonably high level of quality, you can then promote your content to websites who have online business authority.
If a highly reputable site links to your webpage, then you get a quality backlink.
Talking about trust…what about distrust?
Now if a lack of trust is perceived by Google towards your website, then it can reflect negatively on your SEO efforts.
Another way through which search engines can find your website is if other websites are linking to it.
It is also possible to directly submit your site to search engines, but it is probably not necessary for you to do that.
Instead it would be more worthwhile to register your website with Google webmaster tools. Bing and Google use a crawler known as bingbot and Googlebot respectively, that spider the web to look for new links.
These bots might find their way to the link to your homepage and then index and crawl through the pages of your website as long as all the pages on your site are linked together.
If your site has an XML sitemap, then Google bots will use that to index all the pages on your website.
A widely held belief amongst many webmasters is that Google does not permit new websites to rank high in for competitive searches until your web address ‘ages’ and acquires trust in the eyes of Google.
Some misconceptions and unknown facts
Sometimes your website might rank high on Google SERPs instantly and then disappear for months. Think of this is as your honeymoon period with Google. When Google bots crawl the pages on your website and index them, your website gets classified by Google.
This classification can have substantial impact on your rankings. Ultimately Google wants to figure out what the intent of your website is.
It wants to know whether you created a website with the sole purpose of it being an affiliate site for Google, a domain holding page or a small business with a definite purpose.
These days it is important that your website conveys that yours is a legitimate business with clear intent and more importantly a website looking to satisfy their customers, if you want it to rank highly on Google SERPs If a page is created solely for the purpose of making money by benefiting from free traffic provided by Google, then such a page could be classified as spam, especially if the content is ‘thin’.
Ensure that the textual content you use on your website and the links provide transparency to Google about the type of business you are, how you function and how you are rated online as a business.
Google will rate your website based on this transparency that you provide on your website.
Using keywords, not just links, to bump up your SEO
If you want to rank for a particular ‘keyword phrase’ search, you must include the keyword phrase or relevant words in your content or have links that point to your website or webpage.
While it is not necessary that you use all the words in the keyword phrase together in your content, it is still generally advisable that you do so.
Ultimately, the steps you might have to take to compete for a specific keyword could depend on what your competition is doing to rank for that keyword.
If you cannot come up with a unique SEO strategy that assists you in leapfrogging your competition, you will have to at least rival how hard they are competing to stand a chance.
If quality external sites are linking to your website, it assists you in having a specific amount of ‘real’ PageRank that is shared amongst all the internal pages in your website.
In future, this will assist you in providing a signal to where a page on your website ranks on Google.
To achieve a more significant PageRank you will need to build a higher number of quality links (or Google juice) to your website, also known as trust or domain authority these days.
Let’s talk a bit about Google and its fiddly algorithm
Google is a link based search engine. Google algorithms cannot actually tell whether the content uploaded on your website is good or quality content.
However, Google understands if the content uploaded is ‘popular’ or not. Also, it recognises poor or inadequate content and can penalise a website for it.
How? By simply making an algorithm change that can take away all the traffic the website once enjoyed.
Any queries sent to Google enquiring about this sudden drop in rankings will be answered with a simple “our engineers have gotten better at detecting poor quality content and unnatural links” kind of reply.
If you have purchased links for your website and been penalised for it by Google, then it is termed as ‘Manual Action’ and you will be notified about it once you sign up in Google webmaster tools.
Website optimisation
For onsite optimisation, try to link the pages with main content text to other pages in the website. And remember, if you get a backlink too, one link from a website with a very high DA is much better than five links from a website with a shoddy DA.
However, we strongly advise you to do this only if you have pages that are relevant to the main content of the original page.
Usually we try to link pages only when there is a keyword in the title element of both the pages. We strongly advise against using auto generating links.
In fact, Google has penalised sites in the past for using auto link plugins.
Therefore, it is best to stay away unless you want to fall on Google’s radar. If you want to rank high for a specific keyword or phrase, then you can try to link to a page with the exact key-phrase in the link.
This technique can help you boost your rankings across all search engine platforms.
However, it is important to remember that post 2016, Google is looking to aggressively penalise optimisers who are using manipulative anchor text.
Look to be sensible and try to stick to plain URL links or brand mentions that will assist you in building brand authority for your website in a less risky manner.
How to insert links naturally within your content and why
Anchor text links in internal navigation can still provide value to your website from an SEO expert perspective as long as you try to keep it natural.
Google needs to find links so that they can categorise the pages on your website.
The SEO value of a cleverly placed internal link should never be underestimated. However, ensure that you do not overdo it.
Too many links on a webpage can contribute towards poor user experience which can in turn offset all the benefits you were getting and perhaps even setting you back more than what you were gaining in the first place.
How Google interprets those links
Similar to how a human visitor will click on links to open new pages, a search engine like Google ‘crawls’ through all your pages by following all the links you have inserted into your website.
Once the pages are ‘crawled’, it then gets indexed and usually within a few days those pages will be returned on a SERP.
Once Google knows all there is to know about your website, the pages that are deemed to be ‘useful’ from Google’s perspective are retained.
Useful pages retained by Google are usually those that consist of high quality original content or have a lot of high quality inbound links.
All the remaining pages are de-indexed. Too many low quality pages on your site could affect the overall performance of your website in Google SERPs.
Ideally you will have pages on your website that are ‘unique’ and stand out from your competition. This means that the page titles, content and meta-descriptions used in your web pages are all unique.
Remember, Google might not use meta descriptions when ranking for certain specific keywords if they are deemed to be not relevant.
If you are not careful, spammers might use your original content for their own website once they scrape off your descriptions and insert the text as main content in their own website.
There is no point in using meta keywords these days because Google and Bing have both gone on record to state that they consider it as spam.
The analysis of your website will take some time as Google examines all the text content and links used in your website.
Keyword stuffing
You do not have to keyword stuff your content to rank high on a Google SERP. You can optimise the pages of your website for more traffic by increasing the number of times the ‘key phrase’ (and not the keyword) is repeated along with synonyms in links, co-occurring keywords, text titles and page content.
There is no magic formula which states that you have to use ‘x’ amount of text in your content or your keyword density ideally should be ‘y’ amount, to get you more traffic for your website.
The priority should be to include the key phrase in the content naturally and to give your users the best possible user experience.
Ideally you should use a number of relevant unique words on your webpage so that it satisfies as many long tail search queries as possible.
How you link your content is really important.
I know we’ve said it over and over. The linking techniques that you employ will often be considered by Google as a means to classify your website. For example, ‘affiliate’ sites are no longer effective in Google these days unless it has high quality of content and backlinks attached to it.
If you link the content of your website to low quality or irrelevant websites, there is a possibility that it too will be ignored by Google. But this could depend on which website you are linking your content to, or more importantly ‘how’ you link your content.
Most SEO experts believe that who you link to (and who links back to you) is very important in determining a hub of authority for your website.
It is very simple really.
You want your website to be in that hub, ideally in the centre.
As Google gets even better at determining the ‘topical relevancy’ of content in a webpage, how well you link out your pages will play a crucial role in how a particular page is ranking on a SERP.
Traditionally the practice was to include links to external websites on single pages which are deeper within a website’s architecture and not on higher or main pages (home page, product pages etc.) of a website.
The benefit of such a strategy is that your main pages soak up most of the ‘Google juice’ which means that greater traffic will be observed on your more important pages.
This tactic can be thought of as old school, but if done correctly they can still be very useful for your site.
‘Content is king’
You have probably find this phrase repeated often, sometimes annoyingly so, but the bottom line is high quality content will help your website attract what Google terms as ‘natural link growth’.
Too many incoming links to your site within a short span of time can lead to site being devalued by Google. It is best to err on the side of caution and aim for diversity in the links.
This makes it more ‘natural’ in Google’s eyes which mean that there less chances of your page being ignored or penalised in the future.
In 2018, strive for natural and diverse links to rank high in Google SERPs.
Google’s criteria
Google might devalue template generated links, individual pages, individual links or even whole websites if it considers them to be ‘unnecessary’ or an important factor that contributes to ‘poor user experience’ for visitors.
Google looks out for who you are linking out to, who is linking to your website and the quality of those links.
These are important factors (amongst other factors) that ultimately establish where a page on your website should rank on a Google SERP.
What could add to the confusion is that the page which is ranking high on Google might not be the page you want to rank well or it might not even be a page that determines how you will be ranked on a Google SERP.
Once Google establishes your website’s domain authority, the page it finds most relevant or the page with which it has no issues will rank well.
Work on establishing links to your important pages or by making sure that at least one page is well optimised compared to other pages on your website for the most important key phrase. It is important to remember that Google does not want to rank ‘thin’ pages on your website in its SERPs.
So, if you want a particular page on your website to rank well, make sure that it has all the things that Google is looking for which these days are an ever increasing list.
Algorithm updates
Every few months Google updates its algorithms to penalise sites that are manipulating SERP rankings or using sloppy optimisation techniques.
Google panda and penguin were two such updates made by Google to its algorithms.

The true art of SEO is to rank well without being penalised by the ever-evolving Google algorithms, or without being flagged by a human visitor. As you might have probably guessed, that’s very tricky and not at all straightforward.
Remember the web is constantly changing and a fast site contributes towards great user experience. Ensure that you prioritise improving your websites download speeds at all times.
There is no denying the fact that every webmaster has to walk a tightrope these days to optimise their website for search engines.
Read on if you would like to find out how not to topple off the tightrope and be successful in modern web optimisation.
The importance of keyword research
Before you start an SEO campaign, the first step you should take is doing the relevant keyword research and analysis.
Here’s a great video to help:
It is perhaps the ‘whitest’ of white hat SEO techniques, a hundred percent Google friendly and will always guarantee you positive results if done correctly.
The chart above shows a page which was not ranking well for a long time, but one we believed that could and perhaps should rank well in Google by just using this simple ‘trick’.
This is possibly the most basic illustration we can provide of a crucial aspect of on page SEO, a technique that is 100% white hat and one that will never ever get you in the docks with Google.
This technique or trick should work for any key phrase on any website. However, the results might obviously differ based on the quality of your content, the user experience your page is providing and the strength of competing pages in Google SERPs.
Let us just clarify that we did not use any SEO gimmicks like redirects or any hidden technique to get the rankings of the page to go up.
Nor did we add a keyword, key phrase or internal links to the page to give the rankings a boost.
But as you can see from the chart there is no denying the fact that the technique we used delivered positive results.
Anybody can profit from this technique so long as there is an understanding as to how Google works or seems to work, nobody can be absolutely certain about how Google works anyway these days.
So, you are probably wondering what exactly we did to get such an upturn in our rankings, aren’t you?
It is very simple actually, we just did some keyword research and added one ‘keyword’ to the content without contributing to the actual keyword phrase itself (as that can be termed as keyword stuffing).
It can get interesting if you use this technique on a lot of webpages on your website. One of the most important aspects of keyword research is, knowing which unique keyword to add to a page.
This example also provides some clarity as to what Google means when it asks for ‘relevant’ content.
In this instance, relevance was achieved by adding the right keyword to the page. Of course it is not the keyword research itself that produces the result, there might be other things happening at the same time that give your rankings a boost.
You cannot pinpoint the exact reason why a certain page is doing well in Google SERPs every time, but what you can do is count on things that you know will definitely work for your website.
In these times of intense competition, it would be a handy to have a few terms your website can rank for in simple ways that gets your competition scratching their heads in trying to figure how you did it.
There are many tools available on the web to help you do some basic keyword research for your website.
This can assist you in being able to quickly identify opportunities to drive more traffic towards your website.
Google analytics keyword
In the past Google analytics was the best source to look at keyword opportunity for some websites (especially the older websites).
However, all that stopped post 2011 when as part of privacy concerns of its users Google stopped sharing information about which keyword was sending traffic to a website.
Google now encrypts searches that people do by default as long as they are logged into google.com separately through a secure connection.
The switch to SSL search (Secure Sockets Layer) also means that a website will no longer receive ‘referrer data’ from Google, even if a visitor lands on the website through a Google search except in instances of paid Google ads.
This referrer data lets a website know what the visitor typed on Google before landing on their site.
Therefore, these days Google analytics displays a ‘keyword not provided’ message instead.
You can still get access to some of this data if you register for Google webmaster tools.
The information you receive can be combined with the data from Google analytics and analysed. Even then the data you receive (limited as it is in the first place) has often been found to be inaccurate.
The keyword data is still pretty useful and can provide invaluable access to backlink data, which is like gold dust these days.
Free SEO Consultation

Come in for a coffee or schedule a conference call with one of our leading UK specialists.
Get Started Now!Are there any SEO benefits of inserting keywords in a bold or italic font?
Some webmasters believe that inserting keywords in your content in bold or highlighting it with italics can benefit your SEO strategy and boost your rankings on a SERP.
The problem with this theory is that it is impossible to test it, meaning it cannot be verified.
There is a possibility that Google could be using this, along with other signals, to recognise on-page SEO efforts to determine whether or not to punish a site or promote it. By this, we simply mean if Google finds a load of random italics or bold keywords when it’s unnecessary, it could be seen as a pitfall.
Anything that’s obviously there to ‘optimise’ your page can be used against you by Google to filter your website out of its SERPs.
Sometimes we use bold or italics in our content specifically for our users.
However, we only use these naturally when there is something we really want to emphasise.
Websites trusted by Google might just get the benefit of doubt for certain optimisation techniques from Google’s web spam team while mistrusted sites might be treated differently.
Therefore, strive to keep everything simple, useful and purposeful.
Is there an exact number of words or keywords that you can use on a page?
This is probably the one question that always crops up.
There is no specific amount of text that you can use on a page that will be considered as optimal for your SEO strategy. Some SEO experts will sing praises for words crossing the 2k line, whereas some posts are just as effective at 1,500.
The amount of text you will most likely need when creating content for your website will depend on the following factors:
- Your domain authority
- Your topical relevance
- How much competition you have for that particular keyword?
- How competitive is the competition you are facing?
Instead of being preoccupied with the quantity of text on your webpage, your focus should be directed towards maintaining a high level of quality for the content on your website.
We’ll prioritise creating a high standard of original content and then optimise that content with the searcher in mind.
There have been instances in the past where we have observed pages with 50 words outrank pages with 250, 500 or even 1000 words. It really depends. If it’s a graphic-heavy product-page, you don’t need giant blocks of text. However, if it’s an in-depth guide, you’ll write more.
Maybe it’s time to write a bit more…
Also, sometimes we have observed that pages with no text rank high on nothing but the number of inbound links to the website or due to the use of some other ‘strategy’.
However, the chances of succeeding with similar strategies in 2018 are very slim as Google has gotten a lot better at hiding or filtering out such pages.
These days we prefer long form pages which consist of a lot of textual content even though we are still heavily reliant on keyword analysis to make those pages.
Longer pages can be beneficial because they are a great way to target long tail keywords or key phrases. Also, creating long information rich pages helps you to focus on producing content that is useful and authoritative.
Every website is different.
Relevance
The most important factor we take into consideration when creating a webpage is to make it as relevant as possible to a particular search query and not focus on the amount of words of MC that the page needs.
Sometimes we might have to research heavily to achieve this, especially if we are unfamiliar with a particular site.
After a while you get a clearer idea of how many words of MC you need to get a page to rank high on a particular domain in Google.
The more textual content you add to a page, as long as it is original, relevant and keyword rich, the more Google will reward you with a larger number of visitors to that page.
Every website and webpage is different.
There is no magic formula stating the optimal number of words that should be used on a page.
The focus should always be on creating original and informative content and not how many words of content you put on a particular page.
Google will always reward you, as long as the content in your webpage is unique and original.
Is there such a thing as the perfect keyword density?
No, there is no such thing as the perfect keyword density.
Again, there is no magic formula or one size fits all equation for the ideal keyword density on a particular page that would guarantee a first page ranking.
What we do know is that if you use a lot of keywords or keyword stuff a page, you will trip a Google spam filter which could possibly lead to a penalty for your website down the line.
Most SEO experts believe that there is no accurate way of determining the ideal keyword to text ratio that guarantees a first page ranking on a SERP.
Search engines are not that easily fooled.
So, instead of looking to manipulate rankings it might be better to focus on doing the little things well, or at least doing them better than your competition.
Prioritise creating original and unique content; all the while keeping in mind the keywords you are focussing on. Ideally you should look to incorporate keywords in a way that is natural and relevant to the content used on rest of the page.
We strive to include synonyms, long term variants and related terms in the MC at least once, as sometimes that is all a page requires to rank high on a SERP.
Maybe before the Google Panda and Google Penguin updates there was such a thing as optimal keyword density, but in modern optimisation there is no such thing and you better be wary if someone is still trying to sell you on the concept of it.
Think ‘things’ and not strings
Google algorithms are no longer reliant on keywords to help them figure out what a page is about and what the page should actually be about to keep a searcher happy.
These days Google relies on information provided by something it calls a ‘knowledge graph’ to create SERPs.
What is a knowledge graph?
The knowledge graph enables a user to search for people, places or things that Google is aware of, like cities, landmarks, sports teams, celestial objects, movies, works of art etc.
For example, let us take a popular search query, ‘Taj Mahal’. If you hear the words Taj Mahal, you would immediately think of one of the wonders of the world situated in Agra, India.
But maybe that is not what the searcher intended when they typed in Taj Mahal in the search engine.
The searcher could actually have wanted to find information about a Grammy winning American blues singer going by the same name or maybe even an Indian restaurant located near to where the searcher resides.
The knowledge graph understands these real world entities and how they are related to each other: Things, not strings. The knowledge graph enhances the quality of a search in Google in the following ways:
Assisting the user in finding the right thing
The English language can be ambivalent or in some instances just plain confusing. Did you mean Taj Mahal the monument or blues musician when typing that particular search query? But with the help of the knowledge graph, Google now understands the difference and can filter down the search results accordingly.
Get the best summary
As Google can now understand or interpret a search query better, it becomes possible for it to provide relevant summary about the search query entered.
For example, type Jamie Vardy into a search bar and you will find information about his age, height, weight, current teams, spouse etc. summarised on the top of a SERP.
Thus, the knowledge graph gives Google a number of options to interpret a search query in a contextual manner by factoring in your search history, how you searched and where you were located when entering the query.
Is it possible to rank highly on Google by writing naturally?
Yes, of course you can. In fact, it’s pretty much mandatory when creating a page for your website.
However, while doing so it is also important to take into account which keywords you are targeting with your content, else you probably would be left behind in the ranking stakes.
If you have not optimised a page for a search engine, you can still rank high by writing ‘naturally’ but only for a few keywords.
These days there are just too many pages competing for rankings in a SERP for you to not optimise the pages on your website.
Generally, the amount of content that you write, the effort you need to put in to do that work and where your page ranks on a SERP can depend on the reputation of the domain on which you are publishing your content.
How can I match what my user wants with my content?
‘What a user wants to achieve’ when typing a particular search query is described by the term, ‘user search intent’. Most SEO experts classify user search intent into the following categories:
- Transactional: The user might want to do a specific thing like; register or buy to fulfil the task they had in mind when typing the search query.
- Informational: The user wants more information about the search query entered.
- Navigational: The user knows where they want to go.
The quality guidelines simplify these into the following constructs:
- Do
- Know
- Go
When creating content for a page your intention should always be to meet the user’s search intent.
As long as you are doing that the number of words you are putting on a page is immaterial. Like we mentioned earlier, someone looking to purchase an item doesn’t need a 2,000 word blog – they want to see a product page. Conversely, someone looking for information on diabetes do not need a product page but rather helpful, non-salesy content.
Optimise your page to enrich searcher intent and user satisfaction
When you are looking to create SEO friendly text for your website, the focus should be on optimising the page for what the user intends when typing a particular search query, and not just the query that the user typed into Google.
Before the panda and penguin Google updates, Google used to send people looking for information on pages that have near or exact matches to the keyword entered.
However, these days Google will send a user looking for information on a specific topic to relevant pages with the highest quality of content that it has on its database.
Google algorithms are constantly evolving, so that it can understand the intent and context of user behaviour better and to that end does not mind rewriting a search query to something it thinks is more relevant and as a result will get more clicks.
This is done primarily to make it easier for a user to find the information they were looking for when typing the search query.
This type of optimisation done for satisfying user intent is something a majority of SEO specialists were already doing even before Google Hummingbird or query rewriting came along.
Optimising your page for the long click
There are many theories doing the rounds for rating ‘user satisfaction’ of which we consider a few to be sensible. It is possible that Google might be tracing user satisfaction by proxy.
For example, if a user has entered in a search query to look for certain specific information, the behaviour of the user from that point on can be used as a proxy of the quality and relevance of the SERP.
What is a long click?
A long click is when a user selects a particular result on a SERP, spends considerable time on that page which in some instances terminates the search entirely.
What is a short click?
If the user selects a result and immediately returns back to the SERP pogo-sticking (going back and forth from a SERP) between other results till the time a long click is observed.
Again, Google can use this information as a proxy for user satisfaction.
Optimising the supplementary content used on your page
Once you are done with the main content, you need to start thinking about secondary links and supplementary content that will help improve the user satisfaction of your page.
Secondary links can also consist of links to pages within your own website. But if your intention is to help the user out in the best way, then you should be linking out your content to more helpful resources available on external websites.
Any website that does not link out to an external website can be interpreted (accurately, some might say) to be self-serving.
Here are some tips on how you can optimise the content on your page better:
- On pages that provide information to visitors, link out to relevant pages on reputable external websites and also link internally to pages on your website with relevant content.
- Add a related products page when creating an e-commerce page.
- Look to create content pieces that provide users with in depth information about the topic.
- Ensure that the content is regularly updated. Also, look to minimise the number of ads used in a page and monitor for redirected or broken links.
- Look to assign content to an author with reliable expertise or online authority in the topic.
- Focus on a wider content strategy for your website and look to avoid creating pages that can be termed as ‘thin content’, six months down the line. If such a scenario does arise, look to combine all the individual blogs into a single piece of content that will provide comprehensive information about a product or service that you provide.
How to create a title tag
The page title tag or HTML title element is one of the most crucial on page ranking factors for a page.
There is no denying that if your page title has keywords, it will boost your chances of ranking high on a SERP.
Also, Google uses this page title as the title of the snippet link provided in a SERP. Here are some factors you should consider, to create the ideal title tag for Google:
- The page title should be relevant to the content provided on that page so as to increase the usability of that page, its click through rate and performance on a SERP. The page title is usually displayed in a browser’s window title bar. The important keyword used on a page should be used at least once in that page’s title tag.
- There is a lot of importance placed on the words within this HTML element by search engines today. A good title should consist of important keyword phrases and should specify user intent clearly.
- Google looks to display as many characters as possible into these clickable snippets which are usually 512px wide and does not include more than one line of text. As a result, there is no specific amount of characters that can be used by any optimiser to guarantee that the title tag will be displayed fully on a SERP. Ultimately, whether or not your entire page title tag is displayed can depend upon the number of words and characters that you use.
- If you want to be absolutely sure that your page title tag is displayed in its entirety in the desktop UK version of a Google SERP, try to create a shorter title consisting of about 55 characters. This does not mean that your title tag must end with 55 characters necessarily. Remember that visitors from a mobile device usually see a longer title. There have been instances where we have seen title tags of up to 69 characters displayed in a SERP. Again, what is displayed on a SERP depends on the number of characters you use in your title tag.
- As we have repeated many times before, all Google cares about is user experience and satisfaction in 2017. So, it is worth noting that usability studies have found that the ideal page title length is around 7 to 8 characters long and consisting of fewer than 64 characters. Longer titles can be difficult to scan into bookmark lists and as a result might not load correctly in many browsers.
- Google might probably index up to 1000 characters in a page title tag, but no one is sure as to how many words or characters Google will consider as a title when evaluating relevance for ranking purposes. Previously, we have experienced some success with long titles. All the words in your title tag will definitely be read by Google irrespective of its length, unless you are looking to spam (which of course is a very silly thing to do these days).
- You could maybe use up to 12 words that will be considered as part of the page title. Try to include an important keyword within the first 8 words of your page title. The rest of your title will be considered as part of the normal content on the page.
- It is important to note that post 2016 the title you choose for a particular page might not be the one Google selects as part of your search snippet. The title and description of the search snippet is very reliant on the query typed these days. Google can now choose your search snippet from other information on the page or from links to that page based on what it considers to be most relevant for the typed search query. As a result, the SERP snippet title displayed on a SERP can be very different from the one you had created for the page.
- The whole point of optimising your title tag is to rank for as many important terms as possible without keyword stuffing your page title tag. Ideally it is advisable to adopt a longer tail approach and optimise only a particular phrase in your page title. It is important to note that using too many title tags without sufficient on page content to back it up can be flagged by the panda update on the grounds of providing poor user experience to visitors. If the page has ‘thin content’, it does not matter how relevant or unique the title tag of the page is. These days Google places a lot of emphasis on the quality of textual content on a page to allow a page with a good title but thin content to rank well on a SERP.
- Some page titles rank better with a call to action that clearly reflects a searcher’s intent. If this call to action is chosen by Google as part of your snippet description, then it is important to remember that your title will act as a ‘hook’ for your page which might just give you an invaluable edge over your competition.
- The ideal title tag for a page is unique to all the other pages on your website. Ever since Google released its panda update in 2011 which focuses on greater ‘quality’ in sites, it has become very important to create unique page titles and reduce any possibility of duplication.
- We prefer to include an important keyword in the page title as early as possible, but even if that cannot be done, you should definitely look to incorporate key phrases or keywords in some part of your title tag.
- Sometimes greater search engine visibility is more significant than branding and therefore the name of brand is incorporated at the end of the title tag. However, if you have a brand that is recognisable, it could be better from a rankings perspective to put it in front of the titles. On some occasions, it does not really matter where you put it because Google quite often changes the title dynamically, putting your brand at the front of your snippet description itself.
- Generally, you would be better off not trying to make your meta-description or title stand out by including special characters, as Google has gotten quite good these days in removing special characters from a page title. Apparently, Google does not want your title tag to include special characters. But it is possible to make your search snippet stand out with a schema mark-up and rich snippets.
- In an ideal situation the page title tag you create is suitable for search engines and human visitors.
- Creating a natural looking title is perhaps better and might continue to get ‘better’ as search engines continue to evolve.
- We generally prefer to use mixed case text for our page titles as we have found it to be more scan-able compared to titles that are all uppercase or lowercase.
- If your domain has a high level of authority and trust in the eyes of Google, it will be easier for you to rank well for a new page. It is important to keep this in mind as there is only so much you can achieve with respect to your rankings with a unique and well optimised title.
- The click through rate (percentage of visitors on a webpage that follow a link to another page) of your page will also be considered by Google when ranking it. So, it might be worth optimising your page titles for better click through rate.
- Google will select the title it deems best for your search snippet and it can take the information from multiple sources and not just your page title tag. If the page title is small, Google might add more information about your domain. If you have a strong brand recognition, Google might replace your page title with that.
Remember when you write a title tag, you have a chance to convey to Google whether yours is a quality or spammy site.
For example, if you have used the keyword 5 times in the title description in a way that obviously resembles keyword stuffing, your website would be considered as spammy by Google, and as a result your search rankings will suffer.
We believe that the title tag should look as natural and unique as possible with the inclusion of a keyword and related term (if possible).
Meta keywords tag
Perhaps the biggest indicator of shady black hat SEO optimisation techniques is the meta keywords tag.
If a part of the optimisation strategy for your website includes using a meta keywords tag, it is high time you realise that your resources and money are being wasted in this futile attempt to boost rankings.
It is best to forget about them as they have no impact on your search engine rankings.
From what we understand both Google and Bing ignore meta keywords, assigning zero weight in them for ranking.
In fact, Google considers this practice as spammy and has gone on record to state that it is not considered as a ranking factor in a Google SERP. If a key part of your ranking strategy involves meta-keyword optimisation, the chances of success for your efforts is non-existent.
We firmly believe that any optimiser should have more important things to worry about rather than pinning their hopes on such a ridiculous optimisation technique.
The funny thing is if every optimiser in the world stopped misusing meta keywords, Google might start looking at them again, but that is just how it is in search engines these days.
We are strictly against the use of this outdated and spammy SEO technique and we remove it from any page we are working on.
Meta description
The meta description is really important, both from a perspective of SEO and human visitors. In HTML the meta description is used to provide a summary of the page’s content.
It is the 160-character snippet that Google uses as part of your search snippet to give users a fair idea about what they can expect on your webpage.
Try to make it look as relevant and appealing as possible so that when a user comes across it they are tempted to click on your page link.
If you have used the same meta description for all the pages on your site, Google has the authority to create its own snippet for your page from multiple sources (open directory project snippet or keywords).
It all depends on what Google considers to be the most relevant way to describe that particular page on a SERP to a user.
So, look to create unique meta descriptions for each page on your website.
If you want your meta description to be used as the snippet on a SERP and have optimised a page on your site for one or two key phrases, make sure that the meta description tag of that page includes the keyword.
Generally, we do try to include a keyword in the meta description as over the years we have found it to be as one of the most effective ways of getting it included in the search snippet.
Nobody is really sure if the meta description tag is considered as a ranking factor on Google. Even if it is a ranking factor, it would not be a very important one.
Even if meta-description tags are not considered an important ranking factor, most webmasters agree that they are very important in getting user click through from SERPs.
Essentially it provides a website with a chance to make a ‘pitch’ to potential clients and let them know what exactly they will find by clicking on the page link.
If your meta description is spammy and if it was used by Google as your SERP snippet, what do you think would be the chances of a user clicking on your link after reading your snippet?
Most users today are wary of clicking on a spammy looking snippet as they have burned their fingers before.
Anyway, merely adding a keyword or two in the meta description, won’t make a bad site shoot up in SERP rankings or get it on page 1 of a SERP.
If there are no obvious SEO benefits, what is the point of optimising your meta description for a search engine? None actually.
Instead, it would be more beneficial for your website if the meta description was made unique and relevant for a human user.
You can programmatically generate meta descriptions on large sites
Some websites find it is easier to generate a unique and accurate meta description.
For example, media websites can easily create a unique meta description for each webpage as all of their content is hand written, so it does not take a lot of effort to create a one line description.
For larger websites, especially those that are database-driven, this can prove to be trickier if not impossible.
Such websites can rely on programmatic generation of meta descriptions for each page.
A good meta description is readable but for websites that need page specific date, use of programmatic generation of meta-description is encouraged.
However, when doing so it is important to remember that if your meta description consists of a long tail keyword that does not make much sense to a user, the likelihood of it being used as a SERP snippet by Google is extremely slim.
Robots meta tag
<meta name=”robots” content=”index, nofollow” />
You can use the above meta tag if you do not want certain pages to appear on a Google SERP but want Googlebot to index the page and not follow any links used on that page.
The above tag provides a specific instruction of nofollow to Google. Similarly, the robots meta tag can be used to provide a variety of instructions.
It is important to note that Google will follow links and index them by default.
Therefore, there is no need to include this command especially if you are not very sure about how it works.
Valid values for the Robots meta tag “CONTENT” attribute include:
- “INDEX”
- “NOINDEX”
- “FOLLOW”
- “NOFOLLOW”
Here we provide a few examples of how you can use this Meta tag
- META NAME=”ROBOTS” CONTENT=”NOINDEX, FOLLOW”
- META NAME=”ROBOTS” CONTENT=”INDEX, NOFOLLOW”
- META NAME=”ROBOTS” CONTENT=”NOINDEX, NOFOLLOW”
- META NAME=”ROBOTS” CONTENT=”NOARCHIVE”
- META NAME=”GOOGLEBOT” CONTENT=”NOSNIPPET”
Goggle will interpret the above mentioned meta tag values in the following way:
- NOINDEX – prevents the page from being indexed by Google
- NOFOLLOW – stops Googlebot from following links in a page
- NOARCHIVE – ensures that a cached version of the page is not available in SERPs
- NOSNIPPET – ensures that there is no snippet displayed below the page on a SERP. It also prevents the page from being cached.
- NOODP – prevents Google from displaying the open directory description of the page as a SERP snippet.
- NONE – same as “NOINDEX,NOFOLLOW”
The robots meta tag is perhaps one of the very few HTML head elements that any optimiser should focus on to manage Bingbot and Googlebot.
It can be a very effective way to control how your page is returned on a SERP. In an HTML page the robot meta tags go in the [HEAD] section.
We have found that anything else that you can add to the [Head] of your HTML page is often unnecessary.
H1-H6 HTML header tags
What are header tags?
HTML header tags are used on a page to distinguish the main heading of a page along with the other sub headings to the rest of the content.
Most webmasters refer to these tags simply as header tags or heading tags.
There might not be any concrete proof available, demonstrating the effectiveness of header tags from an SEO perspective but there is no doubting its effectiveness.
Several case studies have substantiated the importance of using heading tags effectively.
For example, one company helped Motor Cars ltd. improve their SERP rankings significantly by just optimising their header tags to be more SEO friendly.
One keyword in particular jumped by 320 places in the SERPs to reach the top spot. “We do use h tags to understand the structure on a page better.
We do give a slight boost if we see a clear heading on a page, because we can understand the page is exactly about this topic.” John Mueller, Google Switzerland.
Header tags are another important element of your page that you need to get right to create the ‘perfect SEO’ page for your website.
In HTML, the header tags from h1-h6 form a top to bottom hierarchy.
For example, if your webpage is introduced with an h1 tag but followed by an h3 tag, the heading structure will be broken making it unsuitable for optimisation.
Every page should include an h1 tag but ideally not more than one.
HTML 5 allows you to use more than one h1 tag on a page, but it is still advisable to use only one per page and use as many H2-H6 tags as necessary for your page.
We prefer to use H1, H2 and H3 tags on a page.
We have found that on some occasions Google might use your heading tags as page titles if your title element is found to be malformed.
How many words should you include in an H1 tag?
Ideally, the H1 tag should describe the content below in not more than a sentence. Ensure that the header tag is relevant to the content provided below it.
Also, it shouldn’t be keyword stuffed.
ALT Tags
If your page contains an image, the ALT tag should be used to provide an accurate description about the image.
For example, consider that you have an image of an paracetamol tablet on your page because the blog or article you have written is related to it somehow.
It would be hard for Googlebot to see the image and realise that it is an image of a tablet. It needs help in such a situation and you can provide it by including the ALT tag.
<img SRC=”DSC000525” ALT=” paracetamol 500mg pill”>
ALT tags are very important and especially rewarding from an SEO perspective if you get it right. Furthermore, if your page doesn’t load properly or someone is accessing it on a very slow connection, the description provided by the ALT tag is necessary.
It is counted as ranking factor by both Google and Bing.
However, ensure that you do not over-optimise your ALT tag by including a lot of keywords in it.
We have seen many websites being penalised for spamming ‘invisible’ elements on a page.
We do try to include a keyword in the ALT tag (just once) when addressing a page, but the important thing to remember is to not create an alt tag for Google.
Instead the ALT tag should be included to provide a short and accurate description of the image used in the page.
Now if sometimes you cannot be bothered into putting ALT tags for each image (something most of us have experienced), at least use null value or a blank ALT so that visitors can enjoy your page. Use the ALT attribute to describe your image, but if your image is a link to specific page, use the title tag to provide information about it.
The title tag should inform the user about what will happen once they click on the link. For example, if clicking on the image causes it to become larger, your title tag should contain the following: title=” view a larger version of the paracetamol 500mg pill image”
Here’s a quick video on utilising Alt tags effectively:
Link title attributes, acronym & ABBR tags
Does Google consider the text used in the acronym tag as a ranking factor?
Based on the tests we have conducted, we do not think so. Based on how our pages have ranked over the years we have come to the conclusion that Google ignores keywords used in the acronym tag. Here are some of our observations based on a test page:
- Link Title Attribute – No SEO benefit passed from the link to another page.
- Abbreviation tags (ABBR) – No SEO benefit observed
- Image File Name – No SEO benefit observed
- Wrapping words or numbers in script – There may be some benefits.
It is evident that there are many elements on a page that are completely ignored by Google from a ranking perspective while some invisible elements still hold value, such as:
- NOFRAMES – Visible SEO benefits
- NOSCRIPT – Visible SEO benefits
- ALT Attribute – Visible SEO benefits
Unless there is cause to focus on a particular invisible element, we would recommend optimising the <p> tag in your page.
The <p> tag in HTML defines the beginning of a paragraph. If the <p> tag is defined, the browser automatically adds some space. Using the <p> tag enables designers to add some space between elements in a HTML page which is not technically wrong but can sometimes result in an awkward looking page.
This ‘awkwardness’ can translate into confusion when editing the document and can also sometimes lead to unpredicted spacing when the document is opened in different browsers.
However, if used correctly it can definitely provide value from an SEO perspective not by itself, but through the text content specified within it.
Search engine friendly URLs
Search engine friendly URLs are in essence just that – URLs that are simple, easy to read and clean.
It is important to note that you do not need clean URLs within your site architecture for Googlebot to spider your website successfully. That being said, we consider clean URLs as an absolute necessity and have always done so.
Why? That is because we consider clean URLs to be more usable. Do clean URLs give your site a massive boost in Google SERP rankings?
No, in our experience we have found it to have a very secondary effect on SERP rankings, maybe even less, if it is used on its own. However, there are visible benefits of including keywords in URLs.
We believe that there is definitely some SEO value you can receive due to the page name or actual file name and optimise URLs accordingly.
Using keywords in a URL is not just done to make it more SEO friendly. In fact, including keywords in the URL can help a user determine whether the link has the information they need. Therefore, it can help them make up their mind about whether or not they should click on that particular link.
URLs tend to get copy pasted a lot.
If a link on your site has no anchor text, the keywords used in the URL will act as that anchor text.
URLs are also displayed on a SERP and studies have shown that the URL is one of the most important factors considered by a user before clicking on a link.
It is almost impossible to separate a ranking factor and be absolutely certain about the SEO value it is providing. If people are linking to your site (for example, through forums) by using the URL as the link, it can then be possible to detect the SEO benefit of using a clean URL.
In such a scenario, you can be certain about the SEO benefit you are receiving as the keywords used in the URL are visible in the anchor text link to your website.
Sometimes we would like the name of a URL to be identical to the phrase we want to rank for on Google SERPs.
For example, if our blog is titled “The Top 10 most searched terms of Google in the UK, 2016?” the URL will be configured to show https://wearedapa.co.uk/top-10-searched-terms-google-uk-2016/.
It is important to note that even though Googlebot can crawl a website that uses dynamic URLs, many webmasters fear that it can give up if the URL is not deemed important enough or if it contains multiple session IDs and variables.
Therefore, we strive to use clean URLs wherever possible when working on new websites and look to keep it as simple and readable as possible.

Including a keyword in your page URL can be the difference between whether or not your website ranks for a particular phrase on a SERP and it can be especially useful for long tail queries.
Absolute or relative URLs
Relative URLs are shorter than absolute URLs but are considered more convenient (sometimes) than absolute URLs.
An absolute URL has more information than a relative URL.
You can use either type of URL on your website. Our only advice would be to keep it consistent throughout your website whichever one you choose.
Saying that, we do prefer to use absolute URLs on the websites we are working on.
There is no special reason for doing it. It is just a preference.
Google will crawl either of the two as long as the local setup of your site is properly developed.
https://wearedapa.co.uk/2017-handbook-productive-salesperson/ is an example of an absolute URL whereas /2017-handbook-productive-salesperson.htm is the relative URL version of the above mentioned link.
The one problem with relative URLs is that they can only be used on the same server as the page which contains the URL. If you move that page to another website, you will find that the link no longer works whereas an absolute URL would still work.
What should you use for the ideal URL structure – files or sub-directories?
On some of our websites we use sub folders while on others we use files. We have not found any difference between the two in terms of SERP rankings.
Many CMS or Content Management Systems these days utilise sub folders in their file path, so we are pretty confident that Google can handle them both.

In the past we preferred .html files when optimising a new website from scratch because we believed that for search engines they were ‘the end of the line’ and a directory or sub folder was a collection of pages.
The thought at the time was that it would have been easier to make an individual file ‘trusted’ in the eyes of a search engine in comparison to a sub folder.
However, over the years we have found that this is not the case and rankings in a Google SERP is more dependent on how reputable or relevant a page is to a particular query.
Also, in the past, files were treated differently than sub folders in terms of how they were ranked.
Some subfolders in your site might acquire less trust than other sub folders or individual pages or in some cases be ignored completely.
We also felt that sub folders took that much bit longer to be indexed compared to individual pages especially those that were .html pages.
Webmasters usually talk about trusted domains but what they do not usually mention is that it is possible for some parts of a domain to be trusted less.
Google used to treat certain sub folders differently and sometimes it can be worthwhile remembering how certain things were handled by Google – even in 2017.
Some experts say that it is advisable to not create more than four levels of folders in your file path.
Which is better for Google? PHP, HTML or ASP?
Google does not really care which type of scripting language you use for your website, as long as the document is browser compatible.
An increasing number of webmasters today prefer PHP as it can be easier to add server side code to a particular document using PHP.
Does it boost your rankings if your website uses W3C validated CSS/HTML?
Does a page rank higher on a Google SERP just because it has valid code as opposed to pages that might employ a more casual form of coding?
Not really. Google does not actually care whether you have used W3C valid CSS or HTML.
If you are in doubt, just check the top results on a Google SERP and you might probably find pages that contain invalid CSS or HTML code.
Ideally, we would want all our websites to be easily accessible but sometimes they can be difficult to manage especially if you have multiple developers or authors on a site.
However, if your site is designed poorly with a lot of faulty code such that even Google and its browsers cannot read it, then it can prove to be problematic.
Therefore, if possible always demand a minimum level of web accessibility compliance when hiring developers for a new website and look to use valid CSS and HTML.
Using valid CSS and HTML are not exactly required from an SEO point of view, but they are a standard of ideal practice for website optimisation.
We usually advise all our clients to create websites that adhere to W3C guidelines as they assist in ensuring that the website provides a better quality of user experience.
Internal links should point to relevant pages
We look to internally link pages on the sites we are working on, only when we feel that it is necessary and relevant.
We look to isolate relevant links in the text content of a particular page along with the secondary menu systems and webpages that are contextually relevant to each other.
Optimisers should no longer worry about using perfect isolation techniques anymore.
Also, there is no point dwelling on whether or not you should link one category from another as the search rankings boost you obtain is quite often nominal and not as significant as many consider it to be, especially for the size of websites that we usually manage here at dapa.
Likewise, site architecture is no longer something you should obsess a lot about, but we do strive to ensure that all the pages on a site get indexed from a crawl of the homepage.
We also look to emphasise important pages on a site by linking to those pages where relevant. When you are trying to link internally, focus on finding the exact anchor tag match to the page.
There is no specific method that you can use to internally link pages on your website. What works the most for us is to link pages which are relevant without trying to overdo it.
What Are SERP Sitelinks?
If Google knows enough about a website – its history and relationships, it will on some occasions display site links or mega site links below the URL of the particular website in question.
This leads to an upgraded search snippet for the website or webpage on a SERP.
 When does this happen? The display of a sitelink is triggered if Google is confident about the website or webpage you are looking for based on the terms entered in the search query.
When does this happen? The display of a sitelink is triggered if Google is confident about the website or webpage you are looking for based on the terms entered in the search query.
Usually site links are displayed for queries with a strong brand bias or if the name of a specific brand, company or website is entered into the search query.
How can you get Google site links?
The most popular pages on your website could include pages with quality internal/external links or pages that provide great user experience or sometimes even the most recent posts uploaded on your blog. They are the ones most likely to receive a sitelink from Google.
We have to admit though that sometimes the pages returned for a particular query has had us scratching our heads in trying to figure out exactly why Google has selected that particular page.
If there are no sitelinks on your website as of yet, it is important to stay patient and focus on other aspects of online marketing instead, like creating more content, doing some PR or looking to promote a page through social media.
There is no accurate way to be certain as to when your site will receive sitelinks from Google.
It could take a week or even months, but as your site continues to gain popularity, it increases the chances that Google will catch up with it faster. The sitelinks to your website or a webpage that are displayed on a SERP cannot be turned off.
However, it can be possible to control which pages on your website are chosen as sitelinks.
This can be done in Google webmaster tools.
Why you should always link to relevant sites
Linking out to relevant pages on the web is often considered as one of the best methods of on-page SEO.
We usually look to link out to quality external websites with domain authority and trust, so that a user might find the information provided on the external site useful.
We strive to link out to external pages from individual pages of a website we are working on. We do not usually worry about a PR leak or link equity because it can be controlled on a page to page basis.
We have found such a strategy to be effective as it allows us to share any ‘link equity’ we have with other websites but never at the cost of pages in our domain.
Also, Google cares about which ‘neighbourhood’ your site is located at, on the web.
If you are linking out to reputable and trustworthy sites that have an established domain authority, it places your site in a good neighbourhood especially if your website receives links from those websites.
If you are linking out to spammy sites, it places your site in a ‘bad neighbourhood’ as far as Google is concerned and your rankings will plummet accordingly.
Using your blog to link out to external sites can be particularly useful as it can entice users who are potentially interested in your content. We always stress the importance of not abusing the use of anchor text and therefore try to link out to external websites with the help of keywords that a blogger or site owner would appreciate.
The quality guidelines act as a great reference in helping you identify exactly how useful your supplementary navigation options are with respect to whether you link to internal pages within a website or to pages on external websites.
Why broken links are considered a waste of link power?
We always strive to ensure that each page of website we are working on is linked to another page on the website.
This is perhaps the most important piece of advice we can give to any new website owner or SEO firm.
Broken links are a huge waste of link power and can drastically affect your SERP rankings. Therefore, it is important to check your site for them.
If there are many broken links on your website, it means that those links will return a 404 error message every time its clicked on which can hurt your SERP rankings.
Look to link internally to important pages on your website. But use differing anchor text in the in-page text content and the navigation.
Does Google count the second anchor text link on a page?
Does Google count only the first anchor text link on a page?
Some believe that Google counts the link it finds higher in the code if there are two links on a page that go to the same page.
Consider hypothetically, that you took a page and inserted two links on it both going to the same page.
Will Google even read the anchor text of the second link on the page, or will it just count the first link on the page? If Google does read both anchor text links, will you get a ranking boost from both the links or will Google ignore the second link?
What probably makes it more intriguing is that knowing this for certain might lead to another question.
Are the links inserted within your content ignored by Google, especially if the main pages are linked to your navigation array? We believe that text links within a page’s content provide great SEO value.
But does it mean that you should place your navigation below the content to get a more varied internal anchor text to a particular page?
Maybe, but the problem here is that there is no way to be certain about this.
Free SEO Consultation

Come in for a coffee or schedule a conference call with one of our leading UK specialists.
Get Started Now!Can you be penalised for using duplicate content?
Google claims that websites are not penalised for using duplicate content.
Imagine the confusion some webmasters experience when they do in fact get penalised for using duplicate content on their site.
Google might not penalise your website for using duplicate content, but if it considers your website to have ‘thin content’, you will find yourself in a spot of bother as it breaches Google’s performance recommendations for a website.
Therefore, you will be forced to remedy this if you don’t want to be hit with a penalty or to remove a Google penalty, in case your website has already been hit with one.
Duplicate content generally refers to substantive blocks of content within or across domains that either completely match other content or are appreciably similar.
What does this mean for me?
You can no longer republish press releases, posts, product descriptions or news stories and expect to gain traction in Google SERPs.
Remember, if your site is composed entirely of duplicated content, Google does not wish to rank it on a SERP.
Similarly, if you are employing a multiple site strategy to sell the same products, you might cannibalise your traffic as time goes by, instead of dominating a particular niche as was possible before.
A lot of it depends on how search engines manage sites that use duplicate content and the user experience Google wishes to provide to its users.
If you get ‘caught’ with duplicate content on your website, even if you might not be directly penalised for it, the end result might turn out to be the same for your website as important pages that ranked well on a SERP no longer do so and new content might not be crawled as fast as a consequence.
Using duplicate content on your site might also lead to ‘manual action’ for thin content.
In such a scenario, the worst that could possibly happen to your website is being hit by a Google Panda penalty.
We strongly advise against repeating text or content across many pages of your website, even if it is your own.
Is it possible to get double or indented listings in Google SERPs?
What does a double listing mean for your website?
It means that there are two pages of your website in page 1 of a SERP.
In essence, a double listing indicates that there are at least two pages on your website with sufficient link quality to reach the top ten results of a SERP for a particular keyword.
It could also be indicative of Google examining sets of results for example by combining two indexes wherein a website ranks differently in both.
How can you achieve indented listings in Google SERPs? It is possible to get indented listings by creating relevant value driven pages with good structure and quality links from reputable external sites.
Indented listings can be easier to obtain in non-competitive verticals. Ultimately it might just boil down to how much domain authority you have and high relevance for a specific search query.
Redirect Non-WWW to WWW
In SEO, canonicalisation relates to individual pages on a website that can be loaded through multiple URLs.
This can be a problem because if multiple pages consist of the same content, but dissimilar URLs that should go to the same page end up being divided among multiple URLs.
For example, http://www.wearedapa.co.uk can be treated as a different URL by Google than https://wearedapa.co.uk despite it being the same page.
You might probably be dealing with canonicalisation issues for your website, especially if yours is an e-commerce website, and it could be detected even at the domain level.
Basically, you should look to direct all the Google juice to a canonical version of a URL. These days it is considered a vitally important practice especially from a SEO perspective.
Why? Canonicalisation keeps everything simple when you are optimising for search engines, especially Google. When you are linking the internal pages of your website, it is important to note that you should not mix up the two types of www/non-www on site.
301 redirects are white hat and also very influential
Instead of telling Google that a particular page is not here anymore via a 404 or not found error message, think about redirecting the page permanently to a page that is relatively similar so that you can possibly pool link equity that the page might still have.
If you are doing this, ensure that the information and keywords are there on the new page. Many are already aware about the power of a 301 redirect.
Redirecting several old pages to one new page might work as long as the information on the new page is relevant to the redirected page that helped rank the original page.
While there is no doubting its effectiveness from an SEO perspective, it is worth noting that this technique has been heavily spammed since the start of 2016.
In fact, there have been instances where penalties have been transferred through 301s. We would also recommend to not redirect 301s to the homepage of your website blindly.
Also, there is no point in redirecting spammy or low quality links to one URL. Consider your contact page or sitemap if you need a page to redirect some of your old URLs.
We have found that canonicals are just as effective today as they were before, even if sometimes it might take a little while longer to make an impact.
A useful tactic at the present moment would be to combine old, underperforming articles with thin content that have been previously ignored by Google into updated, better quality articles.
Then you can 301 all the pages into a single large source to integrate all the content and link equity. As long as you intend to serve users and provide content that is more up to date, Google has no problems.
The importance of the canonical link element
Over the years, the rel=canonical link element has gained a lot of importance from an SEO perspective.
Google, Bing and other major search engines use the canonical link element to allow a webmaster to specify the exact link or page they want to rank on a search engine from all the other near duplicate or duplicate pages found on their website or on other pages on the web.
For example, consider that you have a page on your website www.buythisproduct.com.
But there might also be alternative URLs for the same page such as buythisproduct.com www.buythisproduct.com www.buythisproduct.com/index.html buythisproduct.com/index.html www.buythisproduct.com/index.aspx buythisproduct.com/index.aspx
Though the links look different they return the same page with the same design and the same content.
It can be confusing for search engines if some of the backlinks go to one URL while some might go to another.
Also, it can create duplicate content issues since all the pages are in essence identical and contain the same content.
In such a scenario you can canonicalise all your links into one link by using the rel=canonical element to let a search engine know that you want only a specific link to be considered for rankings.
Canonicalsing your URLs and linking consistently throughout the site can help you to avoid duplicate content issues for your website. <link rel=”canonical” href=”http://www.buythisproduct.com” /> This simple process can easily prevent your SERP rankings from being affected due to duplicate content issues.
Does every website require an XML sitemap?
What is an XML sitemap?
An XML sitemap is a file on your sever which can assist a search engine to locate, crawl and index all the pages of your website easily. It lists all the URLs for a site with metadata about each URL.
An XML sitemap is especially useful for large websites which have a lot of webpages that either publish fresh content or updates content regularly.
For webmasters using sitemaps is perhaps the easiest way to inform a search engine about pages on their website that can be crawled.
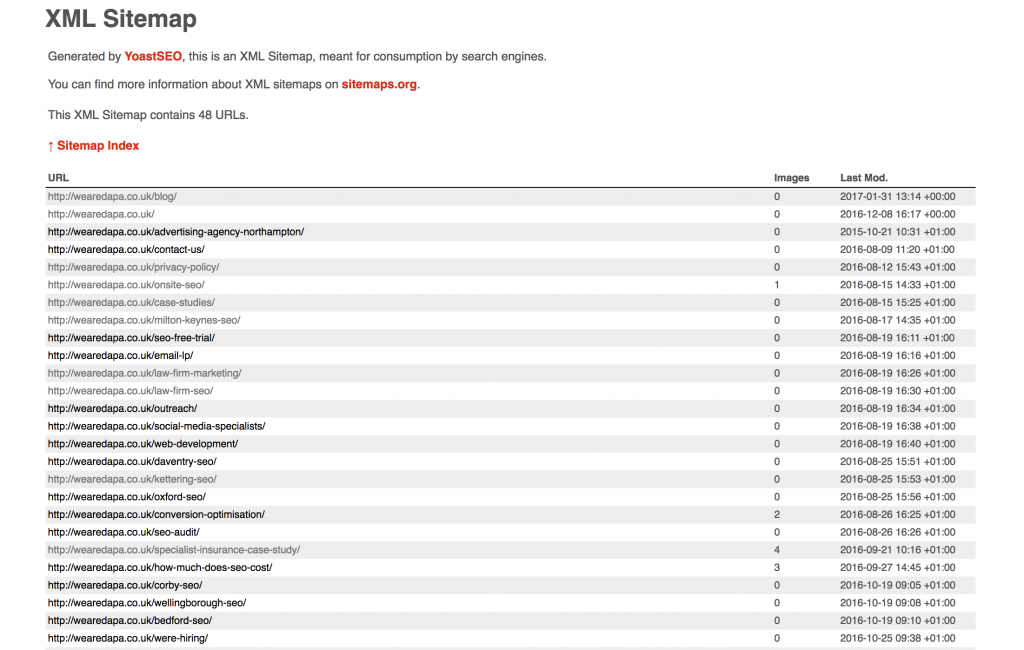
This metadata is used to provide more information about the URL such as when the URL was last updated or how important the URL is or how that URL is related to other URLs in the website.
This ensures that search engines can crawl the pages of your site intelligently.
Do you need an XML Sitemap on your website?
Technically you can optimise your website for search engines even without an XML sitemap as long as you have a navigation system that can be easily crawled by Google so that all the pages on your website are indexed.
However, Google has stated recently that RSS and XML are a useful method for them to discover recently updated content on a website.
Moreover, XML sitemaps have wide adoption and is supported by all the major search engines such as Google, Yahoo! and Microsoft.
Just make sure you:
- Ensure that each page on your website links to at least one other page in your website
- Link to important pages on your website often. You can link the important pages in the navigation or by using differing anchor text or in page content for the best results.
Links are vital for your website to rank well and therefore you must not consider an XML sitemap as an alternative for good website architecture.
Most of the recent CMS can auto generate XML sitemaps, and this can be helpful as Google asks webmasters to submit a sitemap via webmaster tools.
Usually we look to manually define important pages on sites we are working on through the depth of content and links used. But we do recommend using an XML sitemap on your website as we believe it to be the best SEO practice going forward.
Rich snippets
Schema mark-up or rich snippets can sound intimidating especially if you are hearing about it for the first time. But once you understand the concept and method behind it, there is no denying that it will provide you with a boost with regards to your SERP rankings.
Schema markup is basically code that you can use on your website to help search engines provide more informative and useful search snippets to users.
The advantage of using schema markup is that some of the content in your website is indexed in a different way and returned in the form of a richer and more user friendly snippet on a SERP.
This is because the markup tells a search engine exactly what the content means.
Schema markup was made for users and by using it in your website you inform potential users about what your website is about, where you are located, what do you do or maybe about how much your products cost through a richer and more useful search snippet.
In fact, you can think of it as a ‘virtual business card’ for your website. Schema markup can help search engines understand the content of your site better and can help usability which in turn can improve the conversion rate of your website.
The beauty is in its simplicity
Do not look to build your website entirely on flash or HTML frames, especially if you are not fully aware about the evolving accessibility of flash.
Flash is a propriety plug-in and the W3C strongly advises webmasters against using proprietary technology to build an entire site.
Flash can be a great source of rich content for your website. But it might be better from an SEO and accessibility standpoint to build your site using HTML and CSS which will ensure that search engine robots can sample the content in your website.
In the hands of a novice designer, Flash can cause all sorts of problems for your website especially related to:
- Accessibility
- Users not having the Plug-In
- Large Download Times
- Search Engines
Another big problem with flash is that it does not work on some devices like smartphones or the iPhone.
Mobile compatibility
The mobile compatibility of your website is something Google takes into consideration these days and having a lot of flash based content could cause your website to be considered as not mobile friendly on some devices.
It is important to note that Google considers mobile compatibility as a ranking factor since the start of 2016. “Starting April 21 (2015), we will be expanding our use of mobile-friendliness as a ranking signal.
This change will affect mobile searches in all languages worldwide and will have a significant impact in our search results.
Consequently, users will find it easier to get relevant, high-quality search results that are optimized for their devices. These days most designers prefer using HTML5 over Flash.
A site constructed entirely on flash can provide displeasing user experience which can hurt your SERP rankings especially in mobile results. For the same reason, we advise against building a website entirely on website frames.
Site design
So, when designing your site reign in your instincts to go overboard and try to make it as sample as possible. Keeping it simple does not mean you should create basic or boring pages for your website.
Look to make your site as stunning as possible by incorporating the latest graphics, but by using tried and tested methods such as CSS and HTML.
For a novice web designer handling things like JavaScript and Flash can turn out to be a little tricky especially for elements such as tickers, scrolling news etc.
They might look great on TV but can only cause problems to visitors of your website. Ensure that the navigation and layouts used on your website are simple and consistent.
This is also relevant to website optimisation. Ensure that your documents are well structured, the text content and page title elements are relevant, heading tags are used sensibly and look to avoid leaving behind a footprint.
How important is it for your website to download quickly?
Google considers website download speed as a ranking factor.
Even if site speed might not be a big ranking signal and might not give you huge boosts with respect to your rankings, it provides your users with a great user experience.
Coupled with a pleasing UX, it can significantly boost the conversion rate of your website.
Slow loading sites provide users with a poor user experience and as we have made clear in this piece, these days Google and most other search engines care deeply about the user experience a website is providing to its visitors.
There’s a good speed checker below:
Is slow website download speed a negative ranking factor?
“We do say we have a small factor in there for pages that are really slow to load where we take that into account.” John Mueller, Google
Instead of thinking about website speed as a ranking factor it might be more beneficial to think of how a slow loading site can affect your chances of ranking well on a Google SERP.
Slow loading websites are sometimes negatively impacted in Google.
Firstly, if the download speeds of your website are slow, your pages get crawled and indexed slowly.
This can be a big problem for your website, especially if you are regularly updating your content or adding new content to your website.
According to John Mueller from Google, high response time does not affect your ranking ability directly.
Instead, it affects the crawling ability of Google robots on your website.
If only a limited number of URLs are being crawled on your website because of slow load time, it will indirectly affect your SEO rankings. How Fast Should Your Website Load?
As fast as possible. Google likes fast loading sites. In fact, they like it so much that plans are already under way to implement a ‘mobile first’ ranking index. Here’s what they had to say:
“To make our results more useful, we’ve begun experiments to make our index mobile-first. Although our search index will continue to be a single index of websites and apps, our algorithms will eventually primarily use the mobile version of a site’s content to rank pages from that site, to understand structured data, and to show snippets from those pages in our results. Of course, while our index will be built from mobile documents, we’re going to continue to build a great search experience for all users, whether they come from mobile or desktop devices.”
Some non-technical SEO tips
Remember Google is a search engine and wants to provide users with useful and relevant information.
Therefore, Google itself is on the lookout for pages that give users the information they are seeking and to that end wants its SERPs to contain organic results that provide users with value.
Nearly all the websites on the web will link out to sites that contain relevant information, so if your website is rich in content, you will naturally receive a lot of links.
More importantly the links you receive will be considered ‘high quality’ and give you a great boost with regards to your rankings. A glance at the first page of any SERP will show you websites that are rich in content.
High quality content gets you a lot of links and the more link juice your website has the higher it will find itself in SERP rankings.
Ranking organically for a keyword is largely dependent on the number of links your website has as well as how trusted those links are. Some pages can transfer ‘trust’ to another site while some cannot and the same holds true for links.
You need trusted links not just to rank high on a Google SERP, but to also avoid being associated with spammy websites and being penalised as a result.
While Google needs to make money it also needs to ensure that their search engine remains the best search engine in the world and for that they need to make sure that they provide their visitors with value.
Make sure that the website you build provides this ‘value’ to any potential user. Many optimisers are preoccupied with dealing with Google’s ever evolving algorithm, but we instead focus on the idea that gave birth to this algorithm.
Why did Google build an algorithm in the first place? What is Google wishing to provide to its users? What does Google not want to show to its visitors?
Think like a Google engineer and build a site based on what Google is looking to provide to its visitors and you can be confident that your website ranks high and fast.
Google is a link-based search engine and does not require content to rank pages on its SERPs, but it does need content to give to its visitors.
How does Google find content? Very similar to how a user does actually, by following links.
By ensuring that the world knows about your website, you will find that other sites are starting to link to yours.
Are you worried about returning the gesture when high quality or big sites link to your website? Don’t be, by linking back you build a certain amount of domain authority.
Just like with everything else in the world, Google has its limitations.
What are these limitations? How can you go about testing these observations or breaking them and benefiting in the process?
Let’s get this straight, even when you find limitations you cannot be a hundred percent certain about its accuracy regardless of how much you test.
But you could maybe postulate a sensible approach keeping in mind what a Google engineer might do and what you would have done when building a search engine algorithm.
Remember Google does not want anyone to be able to optimise a site perfectly for ranking in its SERPs (who will pay for Adwords if that is the case?). Therefore they’ll strive to create a randomness (at least on the surface) about how pages are ranked.
This helps them keep curious optimisers at bay. At least we believe that is the case. But we also think that this apparent randomness is evidenced in many different ways.
What might boost a particular site’s ranking on SERPs might not work for another website. It might work but not in the exact same manner. Maybe no two sites on the web are ranked the same by Google.
Google results are never constant.
On most occasions a particular page ranks at the top of a SERP because it has more number of trusted and diverse links than perhaps your page does.
It matters where your site is located online whether it’s in a good neighbourhood or a bad one.
Sometimes it feels like Google has a really long memory about the links, associations and pages for your website whereas on some occasions your website might be forgiven for using spammy SEO techniques.
However, even if Google might ‘forgive’ you for spamming, it does not mean that they have ‘forgotten’ your website for using black hat techniques.
There might be a possibility that Google considers varied history versions of a particular page depending on whether you have a blog or an e-commerce website. Decide on the type of relationship you wish your website to have with Google.
Ensure that the onsite SEO practices you employ is legitimate and not spammy in any way so that you make Google think hard about whether or not it should penalise your website for any link discrepancies.
Like most other successful businesses, most of our top clients come from referrals from old clients who ‘trust’ us based on what we have delivered for them in the past.
It might be possible that they heard about us from somewhere else (we are an SEO company after all!), but they trusted us to deliver what they wanted based on the client’s testimonial and referral.
So naturally they have a certain level of trust in us right from the beginning because of the trust they have in the client who referred them to us.
Now when we deliver for them their trust in us grows and now this new client has a greater level of trust in our work. Once a level of trust is established, you have to keep delivering to ensure that the trust level is maintained.
Once you have gained a certain level of trust with Google it is important that you do not do anything to betray that trust.
How how would you feel if a really close friend or family member does something to betray your trust? On some occasions it might be possible for you to forgive them for it, but sometimes it can lead to the trust being eroded permanently.
Similarly, if you look to manipulate your ‘friend’ Google it might result in you losing some or perhaps even all of that hard earned trust.
For example, your pages might still be ranking, but your links might not be considered trustworthy enough to endorse another site. Do not ‘break up’ with Google over something trivial or you might forever end up kicking yourself about that.
Sometimes it just helps to hang out with ‘cooler’ people as it might make you cool by association in the eyes of other people.
The same holds true for Google and its SERP rankings. By making cooler friends (linking to sites with domain authority), you become cooler by association (more trustworthy) in the eyes of Google which benefits your website on SERPs.
Now, if you have managed to earn Google’s trust, it is important to remember that it was made possible because your page gave Google what it wanted in the most profitable way. Your site will be rewarded by Google for helping it fulfil its objectives.
Wondering how Google will reward your website? By adding your website into the list of domains that it trusts the most.
By earning Google’s trust, you will find that your pages are ranking well and you can also in turn endorse other ‘friends’ or pages Google might want to know about.
You can choose to fool or manipulate Google but remember the retribution you might receive could be akin to getting kicked in the unmentionables as probably your friend would do, if you have broken their trust.
Treat Google in the same manner you would want it to treat you and your website.
It takes time to build a level of trust which is also probably why Google considers ‘trust’ as an important ranking parameter these days.
If you incorporate all of the above mentioned non technical SEO tips into your strategy, you can be certain of driving a high amount of traffic to your website from Google over time.
If you are looking to rank high in competitive niches, you might have to be considered a big brand or be linked to by big brands or maybe fake that trust by buying links or by employing spammy techniques, in a way that is intelligent or in a manner that ensures you are not caught (its black hat and almost impossible to execute) by Google.
Things to avoid when optimising your website
Sometimes it is just as important, being aware of which practices you should avoid at all costs when optimising your website.
Just by not doing certain things you prevent the chances of being banned or penalised from Google which in itself is a boost for your overall strategy.
Here we have outlined a few strict no-no’s when it comes to optimising your website:
- Creating a page title that is in no way related to the content used on rest of the page
- Using vague titles like ‘new page 1’ or ‘untitled’ for a page on your website
- Using just one title tag across multiple pages or all the pages on your website
- Creating long page titles that are in no way useful to a visitor
- Inserting (or stuffing) keywords unnecessarily into your title tag
- Creating a meta description that does not accurately describe the content used on the page
- Using common descriptions like “this is a page about football”
- Forming a description that is stuffed entirely with keywords
- Using a common meta tag description to describe all the pages or multiple pages on your website
- Copy pasting the entire content of the page into the meta description tag
- Creating long and complicated URLs that contain unnecessary session ids or parameters.
- Creating common page names like “page2.html”
- Stuffing keywords into the page name in a manner that is very obviously spammy
- Having deep nesting of subdirectories like “…/dir1/dir2/dir3/dir4/dir5/dir6/page.html”
- Naming your directories in a way that makes it irrelevant to the content contained in them
- Having pages on your website from the root directory and subdomains that access the same content
- Combining www. and non-www. versions of URLs into your internal linking architecture
- Using non-standard (or plain odd) capitalisations of URLs. Most users expect URLs to be in lower case
- Making your navigational links complicated for example, linking a page on your site to every other page
- Going overboard with your content strategy. For example, creating content on the pages of your website that is detailed to such an extent that it takes a visitor a lot of time to access the information they were looking for in the first place.
- Creating navigation on your website that is largely dependent on images, animations or drop down menus. If a visitor can access all the pages of your website through normal text links, it makes your site more accessible.
- Ensure that your HTML sitemap does not become outdated due to the presence of a lot of broken links.
- Forming a HTML sitemap that merely lists pages on your website without first organising them
- Permitting your 404 pages to be indexed in search engines. Ensure that your server is configured to return a 404 HTTP status code when a user requests a page that ceases to exist
- Giving a vague message like “404” or “Not found” or none at all
- Designing your 404 page in a different manner than the other pages on your website
- Creating content that is filled with grammatical errors or spelling mistakes
- Embedding text into the images used in a page (remember search engines cannot crawl text embedded into an image)
- Publishing a lot of content on a page without using sub headings, paragraphs or layout separation
- Rehashing existing content or duplicating old articles from your website even though it provides very little value to a user
Some or maybe all of the above mentioned tips might sound pretty basic but often it’s the simple things that trip you up rather than complicated technical techniques.
Often SEO is about making minor modifications to certain parts of your website to get maximum return from a search engine.
If viewed individually these alterations might seem like minor improvements, but when merged with other optimisation techniques they can have a substantial impact on your website’s performance and user experience in organic SERPs.
Avoid making these basic but dangerous mistakes
Ensure that you avoid using duplicate content on your site that is found on other sites on the web. Yes, the ‘content is king’ phrase often holds true from a SEO standpoint. But it is important to remember that the content needs to be unique, original and well linked, to get your site to the top of a SERP.
Never hide text on your website as it could eventually lead to Google removing your site from its SERPs.

Do not buy links from spammy websites and expect to reach the top of a SERP. The chances of being penalised or banned is greater here. Remember Google wants natural link growth and is not in favour of websites buying links to rise up the rankings.
Ensure that every website linking to you is not using the same link phrase or anchor text to do so. This could result in your website being flagged as a ‘rank modifier’.
Always think about the quality of links your website is receiving and not the quantity of links. There is no point chasing Google PR by pursuing hundreds of spammy links in favour of higher quality links.
Do not change your site pages names or site navigation constantly without first employing redirects. This might put you in trouble with nearly every search engine out there.
Ensure that you do not construct your site with JavaScript navigation that cannot be crawled by Yahoo, Google or Bing.
Do not link to every site that asks for links in reciprocity. Ensure that you link out only to trusted websites.
Why poor website optimisation could lead to your website being flagged
The primary objective of using any optimisation technique is to not flag your website as ‘dubious’ to Google’s web spam team or its algorithms.
We strongly recommend that you avoid using tricks like inserting links into H1 tags or linking the same page multiple times with varying anchor text on one page when optimising a page on your website.
Stop thinking about elements on a page based on the SEO value they provide. As long as you are not spamming every element on your page it is going to be useful for you.
By inserting a keyword into every tag, you will once again flag your site as ‘trying very hard’ especially if you do not have sufficient ‘link juice’.
Constantly spamming Google has been often found to be counterproductive in the long term.
Therefore, make sure you do not:
- Spam anchor text link titles by using the same keyword
- Spam your Alt tags
- Spam any other tags
- Stuff your content with keywords
- Create a site for search engine algorithms and ignore human users.
On page SEO is not as straightforward or keyword intensive as it used to be. The smart folk at Google try their level best to make it as complicated as possible.
Still you can follow these guidelines for on-page SEO that will provide you with results:
- Do the required keyword research?
- Identify useful searcher intent possibilities
- Identify your target audience and the purpose of your page
- Create relevant and useful content. Use related terms, plurals and words which describe searcher intent (for example, buy or compare) in your content.
- Decide on a smart page title with possibly a keyword inserted in it
- Create a smart and descriptive meta tag description and repeat it on the page
- Utilise emphasis sparingly to highlight important words or points in the page irrespective of whether or not they are your keywords
- Add an image with a useful alt tag description for a user
- Link your pages to related pages on other sites
- The URL of your page should be simple and Google friendly
- Keep your strategy simple
- Share and promote your content
Why SEO is constantly evolving
These days, SEO consultants need to focus more on each page of the website they are working on, instead of just optimising a page for keywords as was the case in days gone by.
Despite the fact that there are many third party tools or software’s that assist in researching new keywords, most optimisers across the world do not get the kind of access to keywords these days as was once possible.
Proper keyword research is still very important because getting your website on the top of a Google SERP might ultimately boil down to the quality of text content on a page, the usage of keywords in the main content of the page along with the internal and external links.
These signals are considered as the primary indicators when it comes to determining whether your page should rank well, if at all.
It is possible for your site to be hit by a Google filter (for example, Google Penguin or Google Panda) that intend to penalise spam sites in order to provide relevant and high quality search results to a user.
It might also be possible that while one Google filter is ensuring that your page does not rank well in SERPs, another filter is pushing a different page of your website up the search rankings.
There might be mediocre content on certain pages of your website, but the quality of incoming links is pushing it up the search rankings.
On the other hand, there might be instances where you have high quality content on certain pages of your website but still your page fails to rank high because of poor website architecture.
In most scenarios the answer might be the quality of backlinks pointing to the page.
- Does your website not have many quality inbound links?
- Does your website have a lot of low quality (or spammy) backlinks?
- Do pages on your website lack descriptive keyword rich text?
- Is the content on the pages of your website being stuffed with keywords?
- Are you linking out to sites that are unrelated to your specific niche?
- Do you use a lot of ads above the fold?
- Are affiliate links found on every page of your site as well as on the text found on other websites?
- Do you have a lot of broken links and missing images on the page?
It is important to remedy mistakes if any with your website as soon as possible because if you do not do it, your site might be chosen for a manual review by a Google Web Spam Reviewer.
So, it might be just better to optimise your site in the right manner (or at least in a manner that Google finds acceptable) to prevent such an eventuality.
The most important aspect of any successful campaign is convincing Google that your page is the most relevant one for the typed search query.
This can be made possible by getting quality inbound links to your pages along with using descriptive and informative keyword rich text.
The latter as most webmasters would probably agree is getting harder by the day.
How can you know for sure if your page is looking spammy when you are developing it?
Simple really, the next time you open your website look at it from a user perspective and consider if your website appears spammy.
If it appears spammy to you than you can be sure that it appears spammy to Google.
Ask yourself whether all the pages on your website are necessary or relevant.
Which inbound links are received from high quality trusted sources whereas which links are spammy?
Which pages on your website would you ignore if you were a user?
There are many ways you can help (or optimise) a site to rank better but be very careful as any obvious sign of ‘rank modifying’ can put you on the radar of Google’s spam team.
The goal has never been to rank for just the competitive keywords, but to understand why the page we have optimised has ranked high on a SERP.
We look to ensure that each site we are working on provides our target audience and search engines with the best possible user experience.
If you create content that is original, informative and unique to your niche as well as target audience, you will more often than not succeed in your efforts to rank well in organic SERP listings without actually having to use technical optimisation techniques such as search engine friendly URLs or redirects.
Mixing up SEO strategies
There is no one method that can guarantee you long term success with respect to your ranking objectives. So, the focus should always be to create quality user relevant websites with original content that can attract high quality links from sites with domain authority.
Strive to build a website that has real domain authority and provides users with a satisfying user experience. You need to keep mixing up your SEO strategies and learn from past experiences.
Sometimes a Google penalty might not be the worst thing in the world, especially if you can learn from it and avoid making the same mistake again.
There is no point in obsessing about ranking specifics on a granular level that provide marginal return on investment unless you have that much extra time on your hands. We usually find something more worthwhile to focus our energies on.
Free SEO Consultation

Come in for a coffee or schedule a conference call with one of our leading UK specialists.
Get Started Now!Fundamentals
The fundamentals of successful SEO techniques have not altered much over the years, though you can argue that they have become more refined.
Most of the small to medium businesses do not usually require advanced SEO strategies to rank well due to the fact that competing businesses do not employ those tactics either.
On one occasion we took a medium sized business to the top of Google SERPs in a very competitive search niche by simply ensuring that all the pages on the website were well optimised, the home page content text was re-written and by earning a couple of links from trusted sites.
The site we were working on already had a clean record in Google and a few organic links from trusted sources. As the domain of the website already had the authority to rank for important keywords all we had to do was optimise the site for a search engine by altering page titles and improving the quality of on-page content.
We had to deal with certain canonicalisation and duplication issues, but none of those are usually considered major issues by experienced optimisers.
Therefore, by sticking to these fundamental techniques and by not striving for too much, many small to medium businesses can increase the conversion rate of their websites.
Here’s how:
- Ensure that each page on your website links to at least on other page on the site
- Link to the important pages on your website often
- Do not just look to link internally through the navigation, but also through text links that are keyword rich in the main content of a page. Ensure that the internal linking is done naturally and does not appear spammy to a visitor.
- Look to ensure that each content and page element is as unique as possible.
- Build a site for human visitors and not just for search engines.
- Ensure that content created is keyword relevant on sites users might link to.
- Monitor the sites you are receiving links from and also sites that you are linking out to.
- Look to locate places on comparatively trusted sites from which you can get rich inbound links to your website.
- Monitor stats and stay abreast with the latest SEO trends
- Eliminate or at least minimise thin or duplicate content.
What next?
Once you have taken care of the above points, look to create more and better content for your website (you can never have enough content) and promote it so that more people are aware about it if you want Google to give your site more attention on its SERPs.
Time and again we have seen that many websites just need to stick to the basics to be successful on Google.
You might have to use the odd redirect every once in a while, but that’s not exactly rocket science now, is it? It would be much more beneficial if you focus on getting the little things right instead of trying and failing to execute advanced SEO techniques that you might have read about in some blog.
Such a strategy can be more cost effective, productive and safer for your business.
Be aware of pseudoscience preachers
Be wary of people who try to mislead you with what they claim is the ‘science’ of SEO.
SEO is no science especially when you have an overlord (Google) who has total control over the rules and can alter them whenever they want.
For us, optimisation is more about the following factors:
- Researching Google rankings constantly.
- Keyword research.
- Scrutinising why some of your pages are ranking well and why others are not (in a controlled environment of course).
- Inserting relevant words that you want your website to rank for into the content of your pages
- Inserting relevant keywords into the links to the pages you want to rank for in a search engine.
- Understanding that what you have put in your page title tag is what you are going to be ranked for.
- Getting quality and relevant links pointing towards your website.
- Inserting keywords or phrases into the links of the pages that you want to rank on a search engine for.
- Getting trustworthy links from sites that have real domain authority.
- Publishing a huge amount of fresh and original content
- Focusing on long tail keywords
- Most importantly understanding that it takes time to achieve all your objectives and beat your competition with SEO.
Your site is likely to be demoted or penalized if you:
- Insert multiple links with identical anchor text pointing to a page.
- Stuffing a page with keywords to such an extent that it appears incoherent.
- Looking to manipulate Google with spammy SEO techniques
- Optimising more for search engine algorithms rather than human visitors.
- Accepting links from non reliable sources.
- Buying links from shady online SEO ‘companies’.
The biggest challenge we face when optimising sites in today’s SEO climate is to get sites with domain authority to link back to our sites.
However, we have found the reward to be worth the head scratching effort. To achieve this, you should look to invest in content that is marketable or provides incentive for the linking site.
Over the years we have found adhering to the basic SEO strategies such as link building, creating original unique content and finding ways to monetise the content better (without spamming of course) to be more rewarding with respect to our long term goals.
One strategy that works for us is updating our old articles with fresh information as long as the information is accurate or verifiable.
Do not be obsessed with search engine algorithms
Coming up with creative solutions to take advantage of opportunities by doing the right amount of research for your particular niche, you can take advantage of possible ranking opportunities.
Being aware of the latest trends is important but remember if Google finds out that a new strategy is working, it will be quick to roll out an algorithm update that intends to penalise sites that employ that particular strategy. So, wait before you jump onto the latest SEO fad.
The biggest advantage any SEO practitioner can have is the knowledge of what not to do that is resource and experience. Having that knowledge can prevent an optimiser from trying out methods that are bound to alert Google’s spam team.
It will help them create a strategy that focuses on achieving trust and long-term gains over short term ranking boosts.
Getting to the top of a Google SERP could be considered straightforward, if not for the constant rule changes and algorithm updates.
Professional SEO is about possessing a range of skills, techniques, methods and most importantly, it is about having the right experience.
It is more a flexible approach to handle things rather than a one shoe fits all magic formula.
After years of trying out various strategies, we believe that SEO is more about doing the little things correctly for a long period of time.
It takes time to build relevance, trust and domain authority, but that’s how Google wants you to do in order to be successful.
If any company is guaranteeing you immediate SERP success with a magic one size fits all strategy, you better look out.
We would recommend that you check whether this ‘magic formula’ adheres to Google recommended guidelines.
How long do I have to wait for results?
It depends on the SEO strategy you are implementing. Some results can be achieved within weeks while some might take months to show noticeable benefit.
Remember, optimisation efforts to take time.
Some critics believe that this is because Google wants companies to buy their own Adwords to be visible on their search engine.
If you are going down the SEO route, it is important to remember that it is not a process that guarantees quick results.
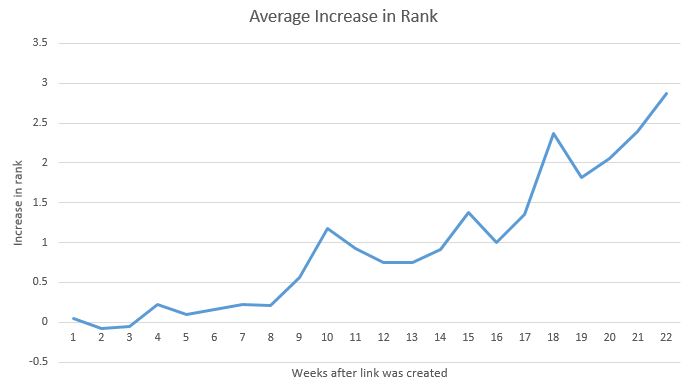
It might take many months (or even years) to judge whether a particular SEO campaign was successful or not.
Fast ranking websites usually find a way of alerting Google’s spam team – so be cautious.
But if you take the time you can be assured of a handsome long-term reward for your business from Google.
Progression of a successful SEO campaign can depend on the following factors:
- How old is your website in comparison to those in the top 10 of a SERP?
- How many back-links does your website have in comparison to those websites?
- What is the quality of your back-links compared to the other websites?
- What is the history of websites linking back to you?
- How useful and relevant is your website as a resource?
- Is your site attracting back-links naturally without having to rely on your agency?
- How unique is the content uploaded on your website?
- Are you paying people to link to your website (which can be grounds for a penalty) or do you have a ‘natural’ reason why people are linking to you?
Google only wants the best for you…
Google wants to return only the best quality pages in its search results and it takes a lot of time to build that level of quality or sometimes just to be recognised for the level of quality you are providing.
Balancing your content, generating high quality backlinks and taking care of broken links all require a certain amount of time.
Google knows the value of its organic listings, which is why they are adamant webmasters work hard and invest a lot of time to rank organically on its SERPs.
To hire or not to hire?
Critics of SEO might say that it costs more to hire an expert SEO compared to the reasonable looking Adwords. But it is important to remember that the price of Adwords is bound to get more expensive as competition increases.
Therefore, sooner or later you will have to focus on building a quality, search engine optimised website in order to be competitive online.
If you start today and are adamant about creating an online brand and a website offering useful content along with a pleasing user experience to visitors, you will be rewarded in Google’s organic listings.
Return on Investment
Ultimately website optimisation is a marketing technique like any other and there can be no absolute guarantees for success.
There can be no guarantees of Google Adwords succeeding either except maybe the costs incurred in competing might rise.
This makes SEO a tantalising prospect, but like any other marketing technique it can still backfire.
Evaluating ROI through SEO can be really difficult even if you factor in all the unknown variables (type of business, website, product, resources, competition etc.) because Google decides where a website should rank on its SERPs.
And on some occasions that might involve ranking better quality websites over yours or sometimes ranking sites that are breaking more rules compared to you.
Every website, every competitive niche is different and that is why there can be no guarantees in SEO despite what some companies claim.
ROI is dependent on multiple factors not least of which is how much your website is suited to convert leads into sales.
What constitutes a spammy page?
When will a page be considered as spam?
- Hidden links or texts-this can be exposed by viewing source code or disabling javascript or CSS or by selecting all the text in a page and scrolling to the bottom.
- Sly redirects- redirecting through multiple URLs, rotating destination domains cloaking with 100% frame and JavaScript redirects.
- Keyword stuffing- inserting so many keywords into the content and links that it appears to be incoherent.
- PPC ads that are designed just to make money and not to serve any users
- PPC ads and copied or scraped content
- PPC ads with feeds
- Doorway pages- a number of landing pages that send the user to the same destination
- Mass produced computer generated pages or templates that contain copied/duplicated content with minor keyword alterations
- Copied message boards with no extra content.
- Fake pages created for a search that contain only PPC ads
- Fake blogs containing copied or duplicated or spun content and PPC ads
- Affiliate pages or sites that exist only to make money
- Pages created purely for PPC ads with no content
- Parked domains
If a page or website exists solely for the purpose of making money and does not provide users with any value, Google considers it as spam.
Any Webmaster looking to make quick money from Google organic listings should keep this in mind. At the very least it should make you think about the type of pages you should create to rank in today’s Google SERPs.

If your page does not provide visitors with any value, you should not expect it to rank in Google.
Is it all doom and gloom though?
Of course not, in fact these rules in some ways level the playing field for everybody.
If you build a website with time and patience looking to be different, unique, remarkable even thinking that you will create unique content that is original and that your website will be attributed as the source of the content, thinking about providing a pleasing and satisfying user experience, in time you will find that you have built a great website that ranks naturally and might even be thought of as a domain authority.
It does not matter to Google who you are, what SEO is, all it cares about is helping users.
If your website is helping users, you can consider yourself on the right path to achieve all your SEO targets.
Doorway pages
Google has already stated on record that they will target doorway pages in their next algorithm update.
What Are Doorway Pages?
Doorway pages are large sets of pages of poor quality wherein each page has been created solely for the purpose of optimising a specific keyword or key-phrase.
In most scenarios, doorway pages are created to rank for a particular keyword or key-phrase and to direct users to a specific destination.
These pages are created for what is known as ‘spamdexing’. Spamdexing is a term used to denote the spamming of the index of a search engine and it is achieved by placing results for a specific phrase in order send the user to a completely different page altogether.
Doorway pages are also known as portal pages, bridge pages, jump pages, entry pages, gateway pages etc.
Doorway pages that are created with the intention of redirecting users without their knowledge use some type of cloaking. They contribute to poor user experience irrespective of whether it is established in one domain or deployed across multiple domains.
Due to this it violates Google’s Webmaster Guidelines.
“Google’s aim is to give our users the most valuable and relevant search results. Therefore, we frown on practices that are designed to manipulate search engines and deceive users by directing them to sites other than the ones they selected, and that provide content solely for the benefit of search engines. Google may take action on doorway sites and other sites making use of these deceptive practice, including removing these sites from the Google index. If your site has been removed from our search results, review our Webmaster Guidelines for more information. Once you’ve made your changes and are confident that your site no longer violates our guidelines, submit your site for reconsideration.”
If you have a lot of doorway pages across a number of sites, you might not want to register at Google Web Toolkit. Here is something Google has said more recently about doorway pages:
“Doorways are sites or pages created to rank highly for specific search queries. They are bad for users because they can lead to multiple similar pages in user search results, where each result ends up taking the user to essentially the same destination. They can also lead users to intermediate pages that are not as useful as the final destination.”
Consider the following as examples of doorway pages:
- Having numerous domain names or pages that are targeted at certain regions to guide users to one particular page.
- Pages that are created to guide visitors into a relevant or usable portion of the site.
- Remarkably similar pages that are near to search results than a browsable hierarchy.
Here are some questions you need to ask yourself to verify if Google will consider a particular page as a doorway page:
- Is the page intended just for optimisation purposes and to guide visitors into actual relevant portion of your website, or are they a vital part of your website’s user experience?
- Does the page consist of duplicated aggregation of certain items (such as products or locations) that can already be found on your site elsewhere for the sole purpose of driving more traffic towards your website?
- Are the pages intended to divert affiliate traffic and guide users along without providing any unique value?
- Are the pages isolated in parts of your site that is difficult to navigate from other parts of your website?
How can you make your website Google friendly?
The definition of a ‘google friendly website’ has changed over the years.
Initially a website was considered to be Google friendly if Googlebot could crawl the pages easily and rank it accordingly.
These days a website can be termed Google friendly if it is accessible, has a high quality of content (that makes it popular) and is built on white hat SEO strategies which ensures that the SERP rankings of the site does not drop dramatically overnight just because Google finds something on your pages that it does not like.
Just providing users with original content is not enough anymore from a SEO standpoint.
It all about how much value your site is providing to users and Google itself.
What or how Google classifies your site is most often considered the crucial ranking factor and this is something that is not often talked about in the SEO community.
Does Google consider your site as a merchant, resource, doorway page, affiliate, spam or crucial to a specific search query?
Why should Google rank your website higher than the sites that are already in the top ten of its SERPs?
Is your website better or are you providing some extra value to customers that other websites are not?
Ask yourself why Google or any other search engine for that matter should rank your website high if it is similar or inferior to sites already on the first page of the SERP.
It is important to think along the lines of ‘how can I make my website better’ than the top ranking sites on a SERP and force Google’s hand in terms of ranking you higher than the other websites.
When building a site, it is important to consider that it might one day be manually reviewed by Google.
The better rankings your website receives or the more traffic you receive will play an important role in determining whether or not your site will be manually reviewed by Google.
According to certain leaked documents, Google sometimes classifies useful sites as spammy. So, if you want to rank high and continue ranking high for a specific keyword or keyphrase, you better provide Google with something other than links to high domain websites.
Google should feel that your website is providing users that they have sent to your page with value and is useful for the kind of information they were searching for.
Remember a useful website is not a website that focusses on a particular commercial intent or one which sends a visitor from Google to another website (also classified as ‘thin affiliate’ by Google).
When building a site, it is important to consider that it might one day be manually reviewed by Google.
The better rankings your website receives or the more traffic you receive will play an important role in determining whether or not your site will be manually reviewed by Google.
According to certain leaked documents, Google sometimes classifies useful sites as spammy. So, if you want to rank high and continue ranking high for a specific keyword or keyphrase, you better provide Google with something other than links to high domain websites.
Google should feel that your website is providing users that they have sent to your page with value and is useful for the kind of information they were searching for.
Remember a useful website is not a website that focusses on a particular commercial intent or one which sends a visitor from Google to another website (also classified as ‘thin affiliate’ by Google).
It is important to take into account what signals in particular Google uses to determine whether yours is an authentic small business website or one that intends to send visitors to other sites with associate links for example on every page of the site.
Do the advertisements on the website be considered as indicators of the webmasters intent behind creating the website?
Google is not exactly going to send you letters thanking you for publishing lots of content, especially if it is a duplicate version of content already available online.
The priority should always be to create original content that provides users with information that they cannot find elsewhere on the web if you want to rank high on a Google SERP.
Make sure that Google is aware that your website is the origin or source of any content that you publish by pinging Google through RSS or XML.
You can also use Google+ to confirm this and we believe that such a practice might gain importance in the coming years.
Understand why Google is ranking other websites (your competition) over you. It is usually because the other websites are:
- More relevant, useful and popular
- More relevant and reputable or
- Exploiting backlinks better than you are
- Using spammy black hat techniques
Keep in mind that all your competition falls into one of the above mentioned categories and looked to create a strategy that can compete with them and in time overthrow them.
How can you ensure that your website is relevant from a search engine perspective?
It might all come down to the key phrases and keywords you use in domain names, URLs, title elements and the number of times they are used (or repeated) in the content of each page, the text in image, alt tags, schema markup and most importantly keywords used in the links to the page in question.
If your SEO strategy is heavily reliant on optimising hidden elements on a page to rank high on a Google SERP than more often than not, you will find yourself triggering Google’s spam filters.
So, it is important to not rely too much on hidden elements of a page to boost your search engine rankings.
Make sure that you create original content and unique page titles for your website. Try to understand how a search engine views your website, how it crawls the pages of any website and remedy broken links or things that might lead to pointless redirects or server errors.
Do those things and you’ll be well on the way to a successful SEO campaign.
 We will get back to you ( normally within 10-30 minutes )
We will get back to you ( normally within 10-30 minutes )